Introduction:
Corneal transplantation, also known as corneal grafting, is a surgical procedure that aims to restore vision by replacing a damaged or diseased cornea with a healthy one from a donor. The cornea, a clear, dome-shaped tissue covering the front of the eye, plays a vital role in focusing incoming light onto the retina, allowing us to see clearly. When the cornea becomes damaged due to conditions such as corneal scarring, infections, injuries, or genetic disorders, vision impairment or even blindness can occur. Corneal transplantation offers hope to those experiencing vision loss by providing a means to replace the damaged cornea with a healthy one, thereby restoring visual function.
WHAT IS A CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION?
Corneal transplant, also known as keratoplasty, is a surgery to replace the diseased/damaged cornea.
WHY/WHAT IS THE REASON FOR CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION?
The cornea is the transparent outer tissue of our eyes. It allows light to pass through our eyes so that we can see. An unhealthy cornea can affect vision by scattering/distorting light and causing blurry vision. A cornea transplant will then be necessary to restore functional vision. During a corneal transplant, the surgeon removes damaged corneal tissue and replaces it with healthy corneal tissue from a donor.
WHO NEEDS A CORNEA TRANSPLANT?
A cornea transplant may improve vision and decrease pain for patients who have corneal damage. Several factors can cause irreversible damage to the cornea, from eye infection to trauma. For the patients who can’t see because of this problem, corneal transplant (keratoplasty) is the only option to restore their vision.
Corneal damage can be due to:
1. Corneal ulcers or scarring
2. Dystrophies (Ex-Fuchs’ dystrophy), an inherited (passed down in families) eye disease that causes corneal swelling and thickening
3. Keratoconus
4. Previous eye surgery complications
5. Swelling or thickening of the cornea
6. Thinning or tearing of the cornea
WHAT IS THE PROCEDURE FOR AN EYE TRANSPLANT?
- Before the surgery, your ophthalmologist may give you calming medication.
2. General anesthesia may be administered to put you to sleep. If a local numbing agent is used instead, you’ll be awake but won’t feel any pain throughout the procedure.
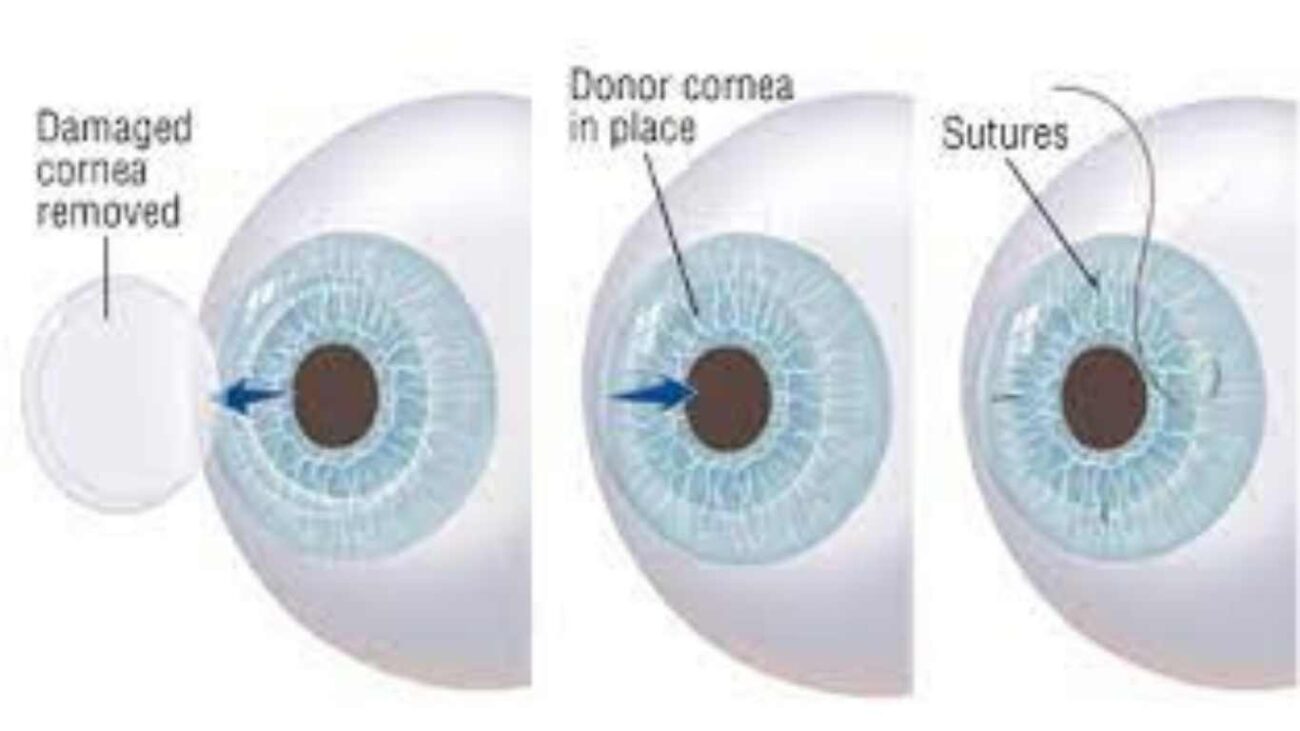
3. Your surgeon will use a special instrument to keep your eyelids open and expose the site of surgery. The exact next steps depend on the type of corneal transplant surgery needed to restore your vision.
4. Generally, only the scarred or diseased part of the eye is removed and replaced with a healthy equivalent from a donor.
5. For any section of the cornea removed, a healthy match from a donor is sewn into place.
6. The fresh site of surgery remains vulnerable to infection and injury for a brief period before healing. For this reason, a protective shield will be placed over your eye after the procedure.
It’s important that you adopt the right self-care practices after surgery to get the best possible outcome. You can discuss these measures with your ophthalmologist before going home.
RECOVERY AFTER CORNEAL TRANSPLANT:
Here’s what to keep in mind to prepare for successful recovery after your corneal transplant:
1. Your repaired corneal tissue is extremely delicate during the first 24 hours following surgery. This wouldn’t be an appropriate time to resume your daily routine.
2. The lack of immediate vision improvement doesn’t necessarily mean that your corneal transplant is failing. It can take a year or longer before your cornea heals and functions as intended.
3. Your ophthalmologist will decide when to remove the stitches from surgery. Your pace of recovery, as observed during routine eye exams, will determine this.
4. You should protect your eyes from physical trauma or any type of external pressure. Wearing eyeglasses or an eye shield is highly recommended.
5. Don’t rub your eye. You will need to use prescription eye drops to control any infection or swelling in the eye.
WHAT IS THE SUCCESS RATE OF CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION?
Most patients with a damaged cornea notice improved vision with corneal transplant surgery. They can enjoy these benefits without any complications for at least 10 years, according to the National Health Service. Treatment success also depends on the corneal disease for which the corneal transplant was done, the type of corneal transplant, and post-operative care.
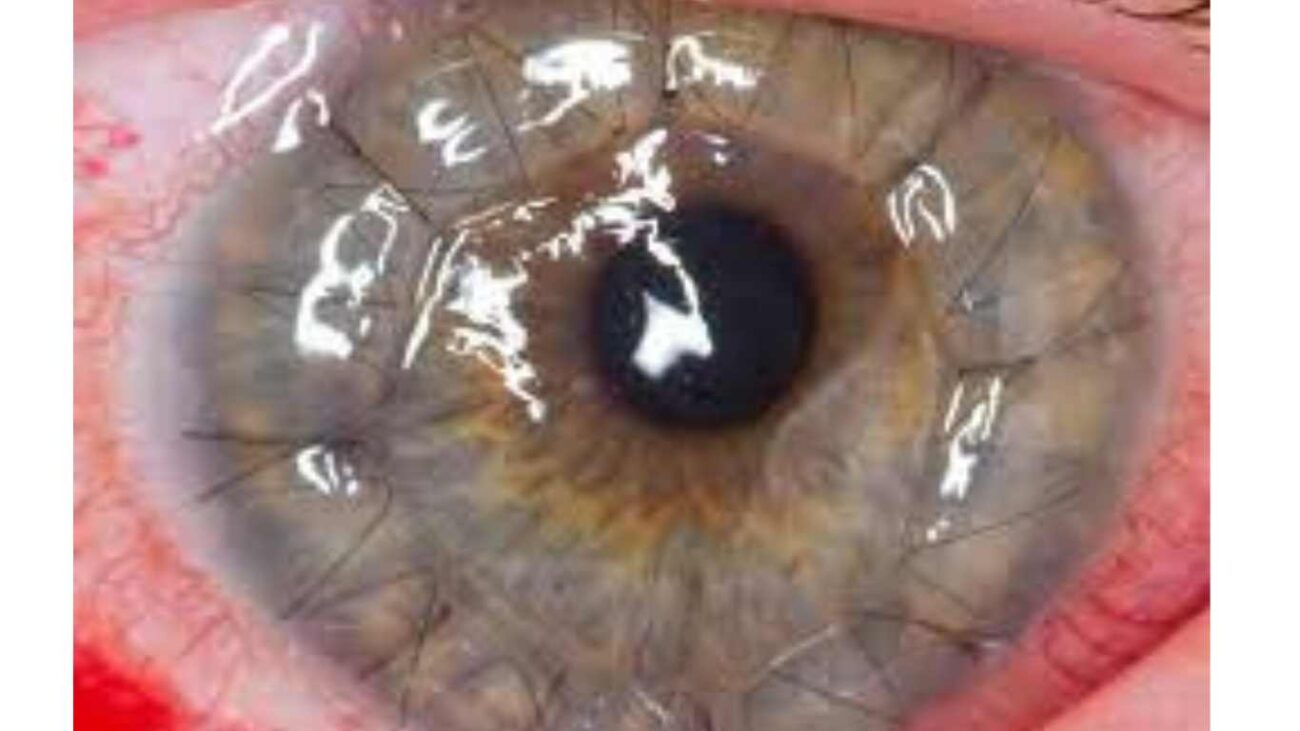
IS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION SAFE?
- Like every other surgery, there can be a few risks associated with keratoplasty.
2. Moreover, graft rejection, which can lead to graft failure, is of utmost importance.
3. In 3 out of 10 patients who have their entire cornea replaced (full-thickness transplant), the body fights and rejects the new tissue. Other types of corneal transplant have a lower rejection rate.
4. About 70% of patients experience no rejection.
5. Other complications include glaucoma, astigmatism, infection
WHAT HAPPENS IF CORNEAL TRANSPLANT FAILS?
- If medication fails to correct graft rejection and failure, the patient may require another corneal transplant or repeat keratoplasty as alternative treatment option.
2. Glaucoma: Keeping your eye pressure within a normal range can prevent damage to your optic nerve.
3. Uneven cornea or astigmatism: To fix this vision problem, your ophthalmologist may loosen or tighten some of the stitches securing your new cornea in place.
4. Infection: Using antibiotics your ophthalmologist prescribed should help prevent or control any bacterial infection in your eye.
WHERE CAN I GET CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION?
You can undergo a cornea transplant/keratoplasty at VijayaNethralaya super specialty eye hospital in Bangalore.
Author details:

Dr. Sinchana Adyanthaya is a highly skilled ophthalmologist specializing in cornea and refractive surgery. She has obtained her MBBS and MS in Ophthalmology and has also completed a fellowship in cornea and refractive surgery. With extensive experience in conducting routine eye examinations, managing post-operative care, and assisting in various eye procedures, Dr. Adyanthaya has successfully handled a large number of outpatient cases and independently performed surgeries. Her contributions to the field include publishing research articles, presenting at conferences, and actively engaging in academic pursuits. Dr. Adyanthaya is committed to delivering top-quality care and enhancing patient outcomes.
Conclusion:
Keratoplasty is a remarkable surgical procedure that offers hope and restores vision to individuals suffering from corneal damage or disease. Throughout this guide, we have explored the intricacies of keratoplasty, including the different types of transplants, advancements in surgical techniques, and the pre-operative evaluation process. By replacing a damaged cornea with a healthy donor cornea, corneal transplantation opens up new possibilities for individuals to regain their sight and improve their quality of life. The procedure has evolved over the years, with advancements in surgical techniques leading to better outcomes, faster recovery, and reduced risks.