Introduction:
In the field of ophthalmology, innovative technologies have revolutionized various surgical procedures. One such advancement is the YAG Laser PI, a cutting-edge technique used for precise and safe eye surgery. This article aims to explore the intricacies of YAG laser PI, its benefits, applications, procedure, and safety considerations.
What is YAG laser PI?
Doctors perform YAG laser PI, also known as YAG laser peripheral iridotomy, as a minimally invasive surgical procedure on the iris to improve eye health and vision. It involves using a YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet) laser to create a small opening in the iris, allowing proper fluid drainage and alleviating conditions such as glaucoma.

What is laser iridotomy?
An iridotomy is a small hole created with the laser beam in the iris (colored part of the eye). The iridotomy allows fluid to circulate freely within the eye, minimizing the risk of a sight-threatening pressure rise. Doctors perform a laser peripheral iridotomy to treat or prevent a sudden rise in eye pressure caused by narrow angles, narrow-angle glaucoma, or acute angle-closure glaucoma. They typically create the opening at the far edge (periphery) of the iris to help open the drainage angle, and the hole remains invisible to the naked eye.
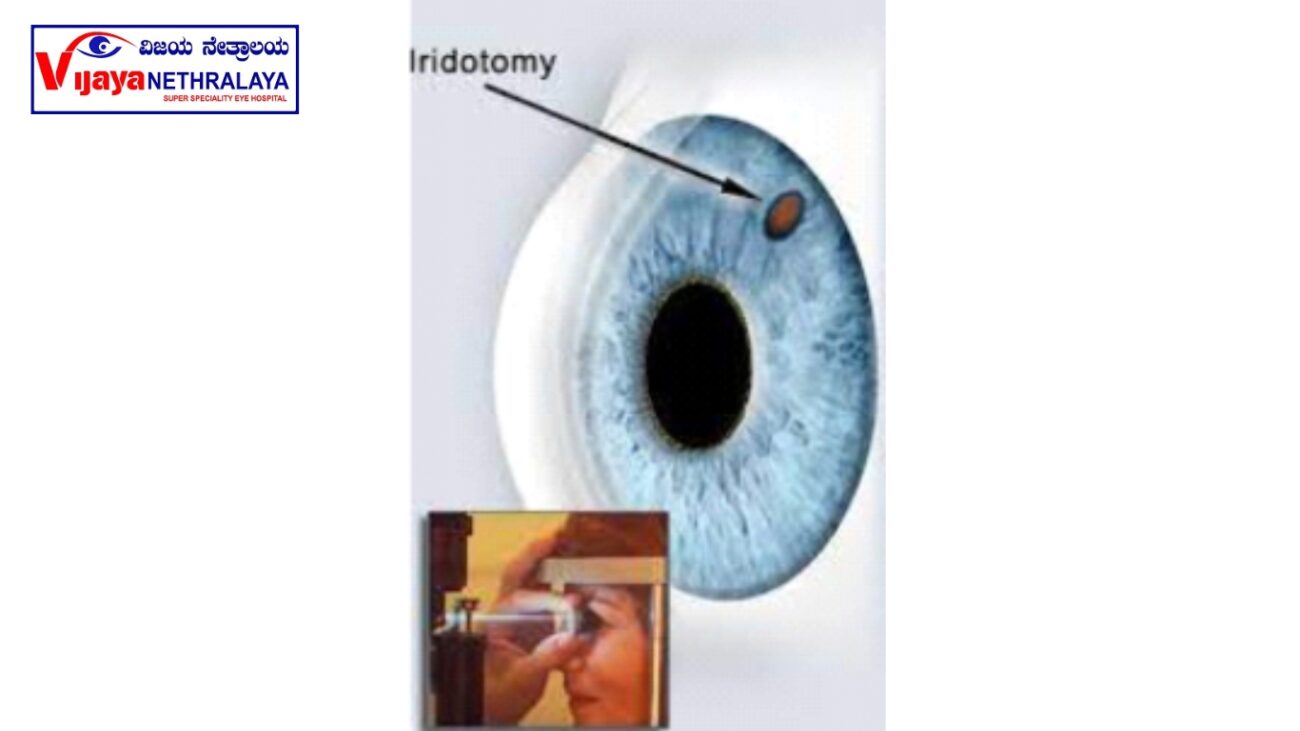
Why do I need this procedure?
1. To prevent an attack of acute glaucoma
2. To treat chronic glaucoma where the drainage channel is very narrow.
3. To treat an attack of acute glaucoma
What are narrow-angle and angle closures?
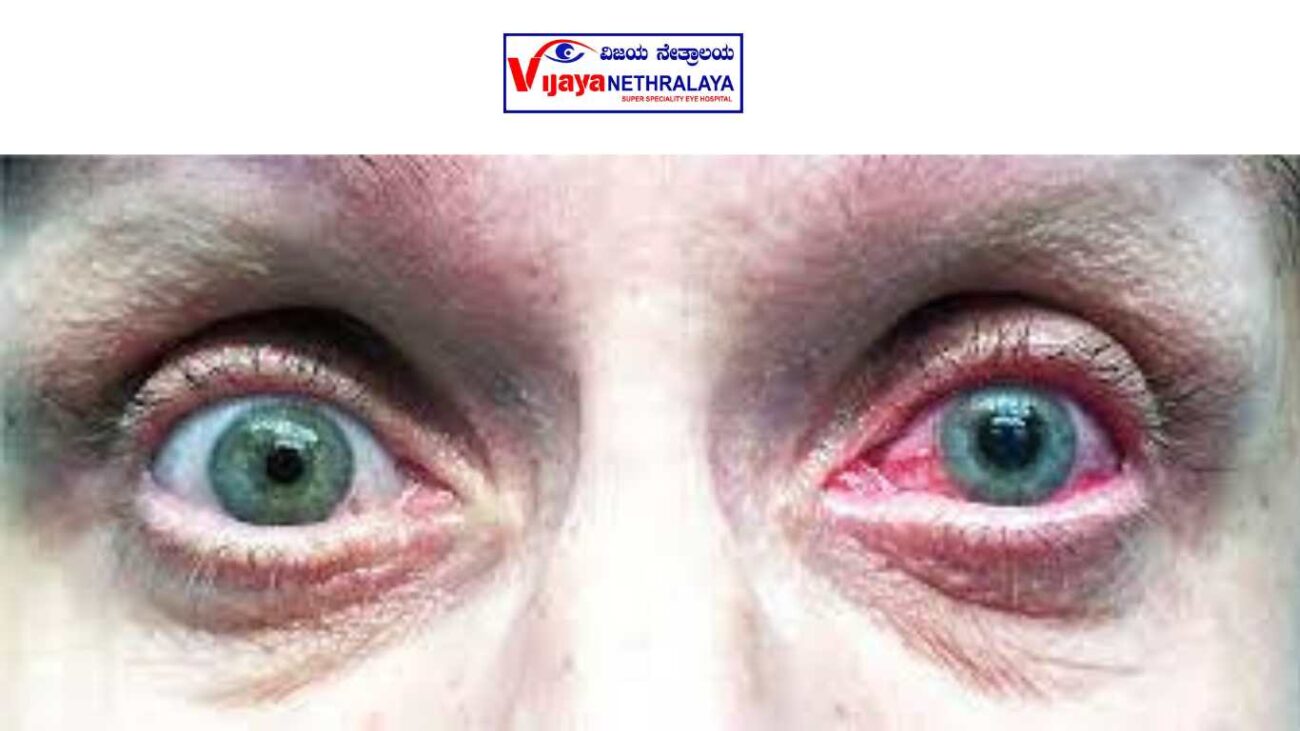
The eye regulates its internal pressure by balancing the flow of aqueous humor. The ciliary body produces this fluid behind the iris, and it flows through the pupil to drain through the “angle”—the space between the iris and cornea. Angle-closure glaucoma occurs when the iris blocks this drainage, causing a rapid increase in intraocular pressure, which can lead to optic nerve damage and irreversible vision loss. There is no cure for this condition. Doctors perform laser iridotomy to create a small opening in the iris, allowing fluid to drain and lowering eye pressure. They also use it as a preventive measure for individuals with “narrow angles,” who are at higher risk of angle-closure glaucoma. A sudden blockage of the drainage angle is an acute angle-closure glaucoma attack, which requires immediate attention.
Symptoms of an attack include
1. Hazy or foggy vision
2. Severe eye and/or brow pain
3. Headache, nausea, vomiting
4. Seeing rainbow-colored rings or halos around lights
An acute angle-closure glaucoma attack is an emergency. It must be treated quickly to prevent loss of vision. Some people do not have symptoms with their closed-angle glaucoma, but high pressure is still damaging the optic nerve. This is called chronic angle-closure glaucoma. This condition often requires surgery.
How is the procedure done?
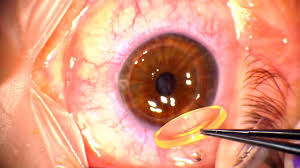
It is an outpatient procedure and normally takes approximately 15-30 minutes. On arrival, you will have a doctor who will explain the procedure and ask you to sign a consent form. The nurse will first apply pilocarpine 2% eye drops to shrink your pupil, allowing better visualization of the iris crypts where the laser will be applied. Then, the nurse will administer anesthetic drops. The doctor performs the procedure with or without a contact lens. During the procedure, you will see bright flashes of light, hear clicking sounds, and may feel slight discomfort as the laser targets the sensitive tissue of the iris. The doctor uses laser pulses to create a small opening in the peripheral iris, enabling aqueous fluid to flow more freely.
What should I expect after treatment?
Your eye may appear pink and feel sore, with temporary vision disturbances lasting the rest of the day. As a result, your doctor will strongly advise you not to drive yourself home. They may prescribe steroid drops for a few days to control inflammation, along with drops and/or tablets to help lower your eye pressure to normal levels. In severe cases, patients may need to have their eye pressure checked a few hours after treatment.
Benefits of treatment:
- Laser treatment aims to prevent raised intraocular pressure and reduce the risk of vision loss from glaucoma.
- When performed at an early stage, there is a 66-75% chance of “curing” the condition.
- In later stages, laser treatment may help slow or stop the progression of the disease.
- Advanced cases may require medication and/or surgery in addition to laser treatment.
- Doctors perform the procedure to save the remaining sight, but it cannot restore lost vision or improve existing vision.
- The primary purpose of laser treatment is to prevent sudden increases in eye pressure.
- Without this treatment, there is a risk of developing sudden glaucoma and irreversible blindness.
What are the side effects?
- Mild, uncommon, and short-lived side effects may occur after YAG laser PI.
- You may experience redness, light sensitivity, and discomfort for a few days after the procedure.
- There may be a temporary increase in eye pressure.
- Blurred vision is a temporary side effect.
- Temporary inflammation of the eye may occur.
- Hemorrhage from the laser hole inside the eye is fairly common, causing misty vision that usually resolves within 24 hours.
- Cystoid macular edema, a swelling in the retina, can occur and may be more frequent in diabetic patients. It can be successfully treated with drops in most cases.
- Less than 1% of people may experience a deterioration in vision following the procedure, with some experiencing glare.
- Doctors may recommend additional laser treatment if the laser hole is not large enough or if it closes up, requiring them to repeat the procedure at a later date.
Eye Words to Know:
Optic nerve: A nerve at the back of your eye that connects to your brain. The optic nerve sends light signals to your brain so you can see.
Aqueous humor: Clear liquid inside the front part of our eyes. Aqueous is different than tears. It nourishes the eye and helps it hold its shape.
Drainage angle: The area of the eye where the aqueous humor drains from the front of the eye.
Author Details:
Dr. Ravina Todi is a talented and dedicated ophthalmologist with extensive experience in treating eye conditions. She holds an MS in Ophthalmology and is highly skilled in various procedures and surgeries. Dr. Todi has actively participated in research, publications, and professional organizations, demonstrating her commitment to advancing the field. Dr. Ravina Todi, a skilled ophthalmologist specializing in glaucoma, is highly regarded in her field due to her excellent patient care and continuous pursuit of knowledge. With an MS in Ophthalmology, she has extensive experience in eye treatments and surgeries. Dr. Todi is dedicated to patient care and advancing the field through research and publications. Her expertise in glaucoma management makes her highly regarded in her profession.