Introduction:
Viral Conjunctivitis, also known as “pink eye,” is a common eye condition caused by viral infection. It affects the conjunctiva, the thin membrane that covers the white part of the eyes and the inner surface of the eyelids. Furthermore, this condition is highly contagious and can spread rapidly, especially in settings where people are in close contact. Therefore, understanding the causes and remedies is essential to manage the condition effectively.
What is Viral Conjunctivitis?
Definition:
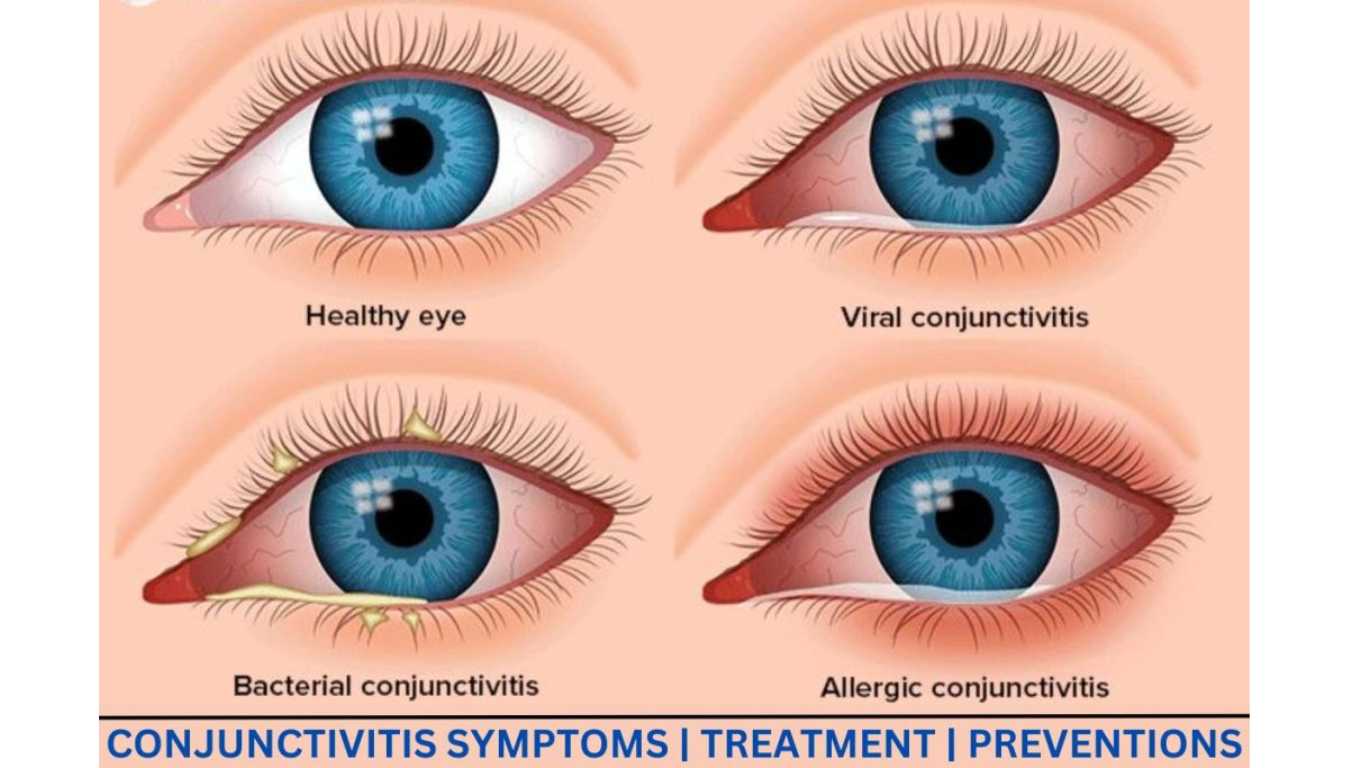
Viral Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, primarily caused by viral agents such as adenovirus, herpes simplex virus, and others. It can affect one or both eyes and often leads to symptoms like redness, itchiness, excessive tearing, and a gritty sensation in the eyes.

Common Symptoms:
The typical symptoms include:
- Redness in the white part of the eyes
- Watery discharge from the eyes
- Itchiness and irritation
- Swollen eyelids
- Sensitivity to light
How does it spread?
It is highly contagious and spreads through direct contact with infected eye secretions or respiratory droplets from infected individuals. It can also be transmitted by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus.
Causes:
Viral Agents:
Various viruses can cause conjunctivitis, with adenovirus being the most common culprit. Herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus can also lead to viral conjunctivitis.
Risk Factors:
Certain factors increase the risk of developing viral conjunctivitis, such as exposure to infected individuals, crowded environments, and poor hand hygiene.
Seasonal Trends:
It often exhibits seasonal patterns, with higher incidences during the late spring and early fall months.
Diagnosing Viral Conjunctivitis:
Clinical Examination:
Diagnosing viral conjunctivitis usually involves a comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist. Firstly, the doctor will assess the symptoms, then proceed to examine the eyes, and inquire about recent exposure to infected individuals.
Laboratory Tests:
In some cases, the doctor may collect a sample of eye discharge for laboratory testing to identify the specific virus causing the infection.
Differential Diagnosis:
Distinguishing viral conjunctivitis from other types of conjunctivitis (bacterial or allergic) is crucial for appropriate treatment.
Preventive Measures:
Hygiene Practices:
Frequent handwashing and avoiding touching the eyes can reduce the risk of contracting viral conjunctivitis.
Avoiding Contact:
Infected individuals should avoid close contact with others to prevent the spread of the virus.
Vaccination:
In some cases, vaccination against certain viruses can help prevent conjunctivitis.
Remedies:
Home Care Tips:
- Applying warm compresses can help soothe irritated eyes.
- Using artificial tears can provide relief from dryness and discomfort.
- Avoiding eye makeup and contact lenses during the infection can prevent further irritation.
Over-the-Counter Medications:
Over-the-counter lubricating eye drops or antihistamine eye drops may help alleviate symptoms.
Prescription Treatments:
In severe cases, an eye doctor may prescribe antiviral eye drops or ointments to shorten the duration of the infection.
Tips for Faster Recovery:
Resting the Eyes:
Allowing the eyes to rest and avoiding activities that strain the eyes can aid in faster recovery.
Using Warm Compresses:
Gently applying warm compresses to the eyes can reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Avoiding Irritants:
Staying away from smoke, dust, and other irritants can prevent additional discomfort.
Coping with Viral conjunctivitis:
Managing Discomfort:
Using cool eye packs and wearing sunglasses can ease discomfort from sensitivity to light.
Supportive Measures:
Staying hydrated and, additionally, maintaining overall good health can help support the body’s immune response.
Seeking Medical Attention:
If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical attention is essential to rule out any complications.
When to Consult an Eye Specialist:
It is advisable to consult an eye specialist if:
- Symptoms worsen or do not improve with home remedies.
- There is a decrease in vision.
- The eyes become very painful or sensitive to light.
- There is a thick yellow or green eye discharge.
Conclusion:
It is a common eye condition caused by viral infection, leading to redness, irritation, and discharge from the eyes. Understanding the causes and remedies for viral conjunctivitis can help individuals manage the condition effectively and prevent its spread to others.
FAQs:
- Can viral conjunctivitis be prevented?
- Practicing good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and getting vaccinated (if available) can, in fact, help prevent viral conjunctivitis.
- Is viral conjunctivitis contagious?
- Yes, viral conjunctivitis is highly contagious and can spread through contact with infected eye secretions or respiratory droplets.
- Can I wear contact lenses during viral conjunctivitis?
- It is best to avoid wearing contact lenses during a viral conjunctivitis infection since it can worsen the irritation and delay recovery.
- Are over-the-counter eye drops effective for viral conjunctivitis?
- Indeed, over-the-counter lubricating eye drops or antihistamine eye drops may provide relief from symptoms; however, they will not cure the viral infection itself.
- When should I seek medical attention for viral conjunctivitis?
- If symptoms persist or worsen, or if you experience vision changes or severe eye pain, it is essential to consult an eye specialist for proper evaluation and treatment.