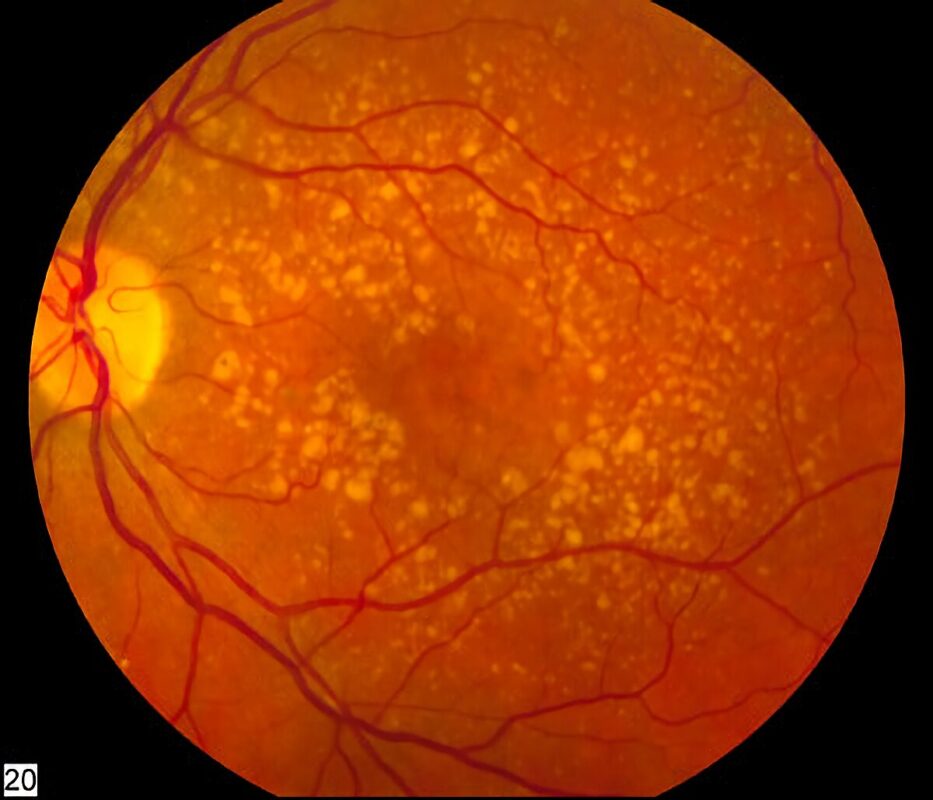
Introduction: Age-related Macular Degeneration (ARMD)
Age-related Macular Degeneration (ARMD) is a common eye condition that firstly affects people aged 50 and above in developed countries, causing vision loss and defects by damaging the macula, which is responsible for detailed central vision this degenerative disease will be the subject of our blog, where we will examine its symptoms, causes, and available treatments

Causes of AMD:
Risk factors increase the risk of AMD.
- Age: AMD is more common in individuals over the age of 50, and the risk increases with age.
- Genetics: A family history of AMD may increase the risk of growing the disease.
- Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for AMD and may advance the advance of the disease.
- Poor diet: A diet low in fruits, herbs, and rutin may increase the risk of growing AMD.
- Cardiovascular disease: High blood pressure, high lipids, and obesity may increase the risk of growing AMD.
- UV light control: control of UV light, particularly blue light, may increase the risk of growing AMD.
Reducing risk factors can help prevent or delay AMD.
Symptoms of AMD:
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) often develops slowly and may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, the following symptoms may occur:
- Blurred or distorted vision: Straight lines may appear wavy or distorted, and central vision may be blurry or hazy.
- AMD can cause difficulty seeing in dimly lit environments.
- Reduced color vision can lead to difficulty distinguishing colors.
- AMD can lead to dark or empty areas in the center of vision.
It is important to note that AMD typically affects central vision, leaving peripheral vision intact. Regular eye exams can help detect AMD early, before symptoms develop, allowing for prompt treatment and better outcomes. Individuals who notice any changes in their vision, including those listed above, should seek medical attention promptly.
Types of AMD:
There are two types of age-related macular degeneration (AMD):
- Dry AMD :
- This is the more common form of AMD, accounting for about 85-90% of cases. Dry AMD occurs when the macula, the central part of the retina, becomes thinner and stops functioning properly. Small deposits of cellular waste, called drusen, may also accumulate in the macula, further contributing to vision loss. Dry AMD typically progresses slowly and may not cause noticeable symptoms until advanced stages.
- Wet AMD:
- This is a less common but more aggressive form of AMD, accounting for about 10-15% of cases.
- Wet AMD causes rapid vision loss due to abnormal blood vessels.
- Wet AMD causes rapid vision loss due to abnormal blood vessels.
Monitoring AMD regularly by an eye doctor is important since both types of AMD can cause significant vision loss.
Treatments for AMD:
There are several treatments available for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), including
- Anti-VEGF therapy can slow AMD progression and improve visual function.
- Laser therapy: This treatment uses a high-energy laser to destroy abnormal blood vessels in the eye. Treating a specific type of AMD called “wet” AMD typically involves the use of laser therapy..
- Photodynamic therapy destroys abnormal blood vessels in the eye.
- Low vision aids can improve visual function and quality of life.
Early detection and prompt treatment are essential for best outcomes, as well as reducing risk factors.
Preventing AMD:
There are several ways to help prevent age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a common cause of vision loss in older adults:
- Eat a healthy diet to protect your eyes from damage.
- Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of AMD.
- Wear sunglasses with UV protection to protect your eyes from sun damage.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve circulation and reduce the risk of developing AMD.
- Monitor your vision: If you notice any changes in your vision, such as blurriness or distortion, seek medical attention promptly. Early detection and treatment can help slow the progression of AMD.
- Manage other health conditions to reduce the risk of AMD.
By taking these preventive measures, individuals can help protect their eyes and reduce their risk of developing AMD.
Why should one consider choosing Vijaya Netralaya for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD)?
Vijaya Netralaya is a renowned eye hospital in India with a team of experienced and skilled ophthalmologists who specialize in the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Here are some reasons why Vijaya Netralaya may be a good choice for AMD treatment:
- Advanced diagnostic technology: Vijaya Netralaya has state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography, which can help detect and monitor AMD in its early stages.
- Experienced ophthalmologists: The hospital has a team of experienced ophthalmologists who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of AMD, using the latest and most effective techniques.
- Comprehensive treatment options: Vijaya Netralaya offers a range of treatment options for AMD, including anti-VEGF therapy, laser therapy, and photodynamic therapy, as well as low vision aids for individuals with advanced AMD.
- Patient-centered care: The hospital’s focus is on providing personalized, patient-centered care, with a commitment to ensuring the best possible outcomes for each patient.
- Affordable treatment: Vijaya Netralaya offers high-quality AMD treatment at an affordable cost, making it accessible to a wider range of patients.
Overall, Vijaya Netralaya is a well-respected and trusted eye hospital with a strong track record of successfully treating AMD and other eye conditions.
Conclusion:
AMD is a common and potentially debilitating eye condition that affects millions of people worldwide. There is no cure, but treatments can slow its progression and improve visual function. Risk factors such as age, genetics, smoking, and a low-antioxidant diet should be taken into account. Regular eye exams can help detect AMD early.
FAQs:
- What is age-related macular degeneration (AMD)?
AMD is a progressive eye disease that affects the macula and can cause vision loss, particularly in the center of the visual field.
- What are the risk factors for developing AMD?
There are several risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Taking steps to reduce risk factors, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and protecting the eyes from UV light, can help prevent AMD.
3. Can AMD be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent age-related macular degeneration (AMD), there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the disease.
4. How is AMD diagnosed?
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) can be diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam, which may include the following:
- Visual acuity test
- Dilated eye exam
- Amsler grid test
- Fluorescein angiography
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
5. Is there a cure for AMD?
Currently, there is no known cure for age-related macular degeneration (AMD). However, there are treatments available that can slow down the progression of the disease and in some cases even improve vision. The treatment options for AMD depend on the type and severity of the disease.
For dry AMD,
- Treatment options for AMD are limited and often involve lifestyle changes like a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking.
- Dietary supplements, including vitamins and minerals, may help slow down the progression of dry AMD.
- For wet AMD, treatment options include injecting medication directly into the eye, photodynamic therapy, and laser surgery.
- These treatments target abnormal blood vessels in the retina, reducing leakage and bleeding that cause vision loss.
- While there’s no cure for AMD, early detection and treatment can slow its progression and preserve vision.
- Regular eye exams are crucial, especially with a family history of AMD or other eye conditions.
- Smoking is a known risk factor for AMD development and progression.
- Smokers are up to four times more likely to develop AMD than non-smokers.
- Smoking damages delicate eye blood vessels, reducing blood flow and oxygen supply to the retina.
- This can lead to abnormal blood vessel development, a characteristic of wet AMD.
- The rate of vision loss in macular degeneration varies based on disease type, severity, age, and overall health.
- Dry AMD usually progresses slower than wet AMD, which can cause rapid and severe vision loss if untreated.
- Early detection and treatment can slow or partially reverse vision loss.
- Regular eye exams and prompt medical attention for vision changes are crucial.
- Our chief cataract surgeon has performed over 100,000 surgeries with precision. Trust your eyes to a skilled expert.