Introduction to Pediatric Cataracts
What Are Pediatric Cataracts?
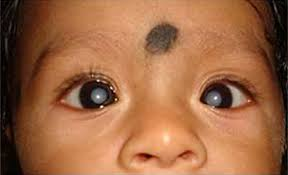
pediatric cataract treatment are cloudiness in the eye’s natural lens that occur in infants or children. Unlike cataracts in adults, they can be present at birth or develop early in life.
Definition and Explanation
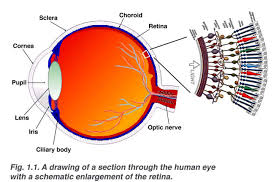
A cataract affects vision by obstructing the passage of light to the retina, leading to blurry or distorted sight. In children, this can severely impact visual development.
Types of Pediatric Cataracts
- Congenital Cataracts: Present at birth.
- Acquired Cataracts: Develop later due to injury, illness, or other factors.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
Early detection is crucial. The younger the child, the more vital their visual development. Delayed treatment can lead to permanent vision problems like amblyopia (lazy eye).

Causes and Risk Factors|: pediatric cataract treatment
Genetic Factors
Many pediatric cataracts are inherited. If there’s a family history of eye conditions, the risk increases significantly.
Congenital vs. Acquired Cataracts
- Congenital: Often linked to genetic disorders or prenatal infections like rubella.
- Acquired: Can result from trauma, steroid use, or other medical conditions.
Environmental and Lifestyle Contributors
Exposure to toxins or malnutrition during pregnancy can also play a role in the development of cataracts.
Recognizing Symptoms:
Common Symptoms in Infants and Children
Look for signs like:
- A white or gray reflection in the pupil.
- Difficulty focusing.
- Squinting or frequent eye rubbing.
When to Consult a Doctor
If your child shows any vision difficulties or abnormal eye appearances, consult a pediatric ophthalmologist immediately.
Diagnosing Pediatric Cataracts
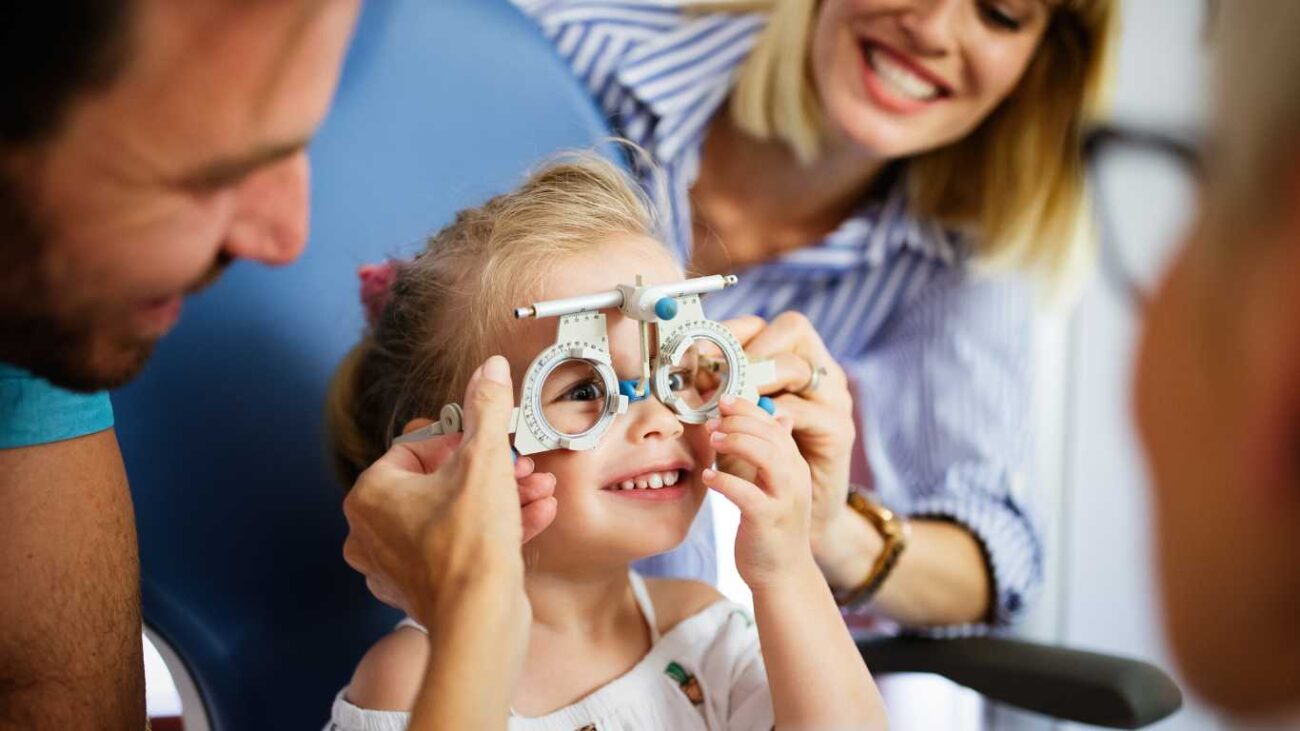
Importance of Pediatric Eye Exams
Regular eye exams can help detect cataracts early, even before symptoms become apparent.
Diagnostic Tests and Techniques
Doctors may use techniques like:
- Ophthalmoscopy: To view the back of the eye.
- Ultrasound: To examine eye structures.
Treatment Options for Pediatric Cataracts
Non-Surgical Management
Monitoring and Eyeglasses
In mild cases, corrective lenses may suffice to improve vision temporarily.
Patching Therapy
Sometimes used alongside glasses to strengthen the weaker eye.
Surgical Options
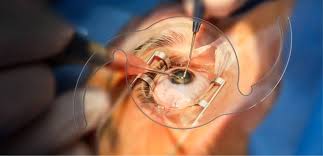
Types of Pediatric Cataract Surgery
Surgery involves removing the cloudy lens and may include replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
Role of Intraocular Lenses (IOLs)
IOLs can provide permanent vision correction, although they’re not always suitable for very young children.
Post-Surgical Care and Recovery
Recovery involves follow-ups and using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and inflammation.
Potential Complications and Risks
Short-Term Risks
These include infection, swelling, or bleeding, which are usually manageable with prompt care.
Long-Term Vision Concerns
Untreated or improperly managed cataracts can lead to conditions like amblyopia or even total vision loss.
Role of Parental Support
Preparing Your Child for Treatment
Parents should reassure their child and explain the process in simple terms to reduce fear and anxiety.
Post-Treatment Follow-Up Care
Maintaining regular check-ups ensures the treatment’s success and addresses any complications early.
Advances in Pediatric Cataract Treatment
Innovations in Surgical Techniques
Modern techniques minimize risks and improve outcomes. Laser-assisted surgeries, for instance, are less invasive.
Emerging Research and Technologies
New approaches like gene therapy hold promise for addressing genetic cataracts in the future.
Importance of Awareness and Education / pediatric cataract treatment
Raising Awareness Among Parents
Educating parents about pediatric cataracts ensures early intervention and better outcomes.
Community and School Screening Programs
Regular screenings in schools can help identify cases early, especially in underprivileged areas.
Conclusion:
Pediatric cataracts are a serious but treatable condition. Early detection and timely treatment can preserve a child’s vision and improve their quality of life. Parents play a pivotal role in this journey, ensuring regular eye exams and supporting their child throughout the process.
Author Details:
Dr. Sushruth Appajigowda holds a prominent position as a Cornea, Cataract, Glaucoma, and LASIK Surgeon in Bangalore. He serves as the chief Cataract and Refractive surgeon at Vijaya Nethralaya Eye Hospital, Nagarbhavi Bangalore. Renowned as one of the finest LASIK surgeons nationwide, he brings with him over 12+ years of experience across multiple LASIK platforms, including ZEISS, ALCON, SCHWIND, AMO, and Bausch and Lomb. Having successfully conducted over 5000 LASIK procedures, Dr. Sushruth holds the title of a Certified Refractive Surgeon and a Fellow of the All India Collegium Of Ophthalmology. Furthermore, he stands as a distinguished speaker at various National and International Forums, using his expertise to guide you in selecting the most suitable procedure based on your health requirements.

http://vijayanethralaya.com/link-in-bio/
FAQs:
- What is the success rate of pediatric cataract surgery?
Pediatric cataract surgeries have a high success rate, with most children achieving significant vision improvement. - How soon can my child return to normal activities post-surgery?
Most children resume normal activities within a few weeks, depending on their doctor’s advice. - Are there any non-surgical treatments for pediatric cataracts?
Mild cases may benefit from glasses or patching, but most cases eventually require surgery. - Can pediatric cataracts come back after treatment?
Secondary cataracts, or posterior capsule opacification, can develop but are treatable with a minor laser procedure. - How often should a child with cataracts have follow-up visits?
Follow-up schedules vary, but regular visits are essential, especially in the first year post-treatment.