Introduction :
The operation of the eye, as incredible organs providing us with the sense of sight, is fundamental for perceiving the vibrant details of the world around us. Understanding the intricate operation of an eye is crucial for maintaining good vision and overall health.
The operation of the eye, akin to a marvel of biological engineering, intricately orchestrates a symphony of processes to enable sight. Beginning with the cornea’s transparent cover, light enters to be focused onto the retina, housing millions of photoreceptors crucial for vision. Through the operation of these photoreceptors, light is transformed into electrical signals, initiating a cascade of neural activity transmitted via the optic nerve to the brain’s visual cortex. Meanwhile, the iris and lens collaborate dynamically in regulating light intake and focusing, respectively, ensuring clarity and precision in visual perception. This intricate operation of the eye not only allows us to perceive the world around us but also underscores the necessity of understanding and preserving its function for overall well-being.
Anatomy of the Eye:
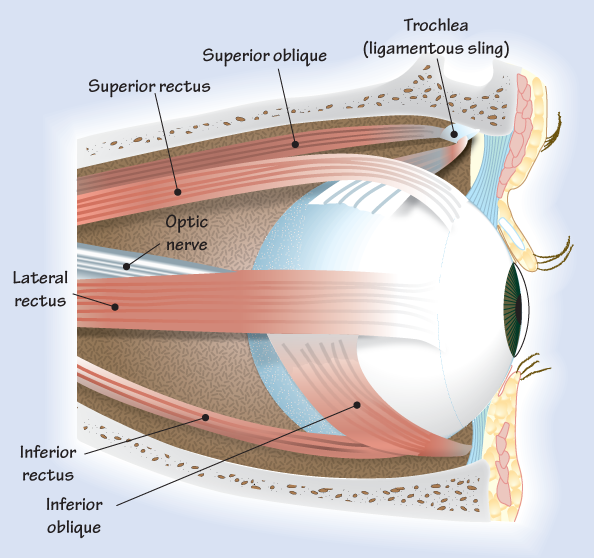
The eye consists of several components, each with a specific function in the visual process. These include the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, and optic nerve. The cornea and lens focus light onto the retina, where images are formed and transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve.
How Vision Works:
Vision begins when light enters the eye through the cornea and pupil. The lens of the eye then adjusts its shape to focus the light onto the retina, which contains photoreceptor cells called rods and cones. These cells convert light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the optic nerve.
Role of the Brain in Vision:
The brain plays a crucial role in interpreting visual information received from the eyes. It processes these signals, allowing us to perceive shapes, colors, depth, and motion. The brain’s visual cortex is responsible for making sense of the images captured by the eyes.

Common Eye Conditions:
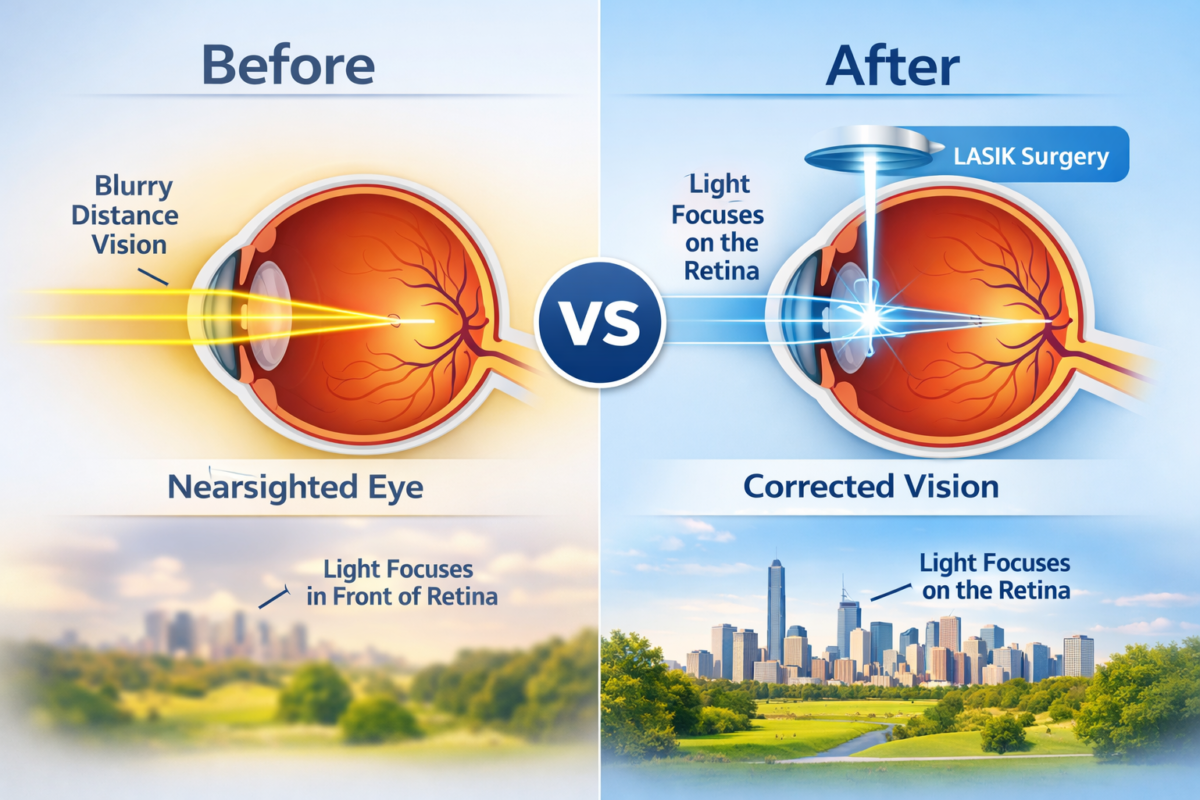
Various eye conditions can affect vision, including myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), astigmatism, and presbyopia. These conditions can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
Eye Health and Maintenance:
Maintaining good eye health is essential for preserving vision. Regular eye exams can detect problems early and prevent vision loss. Additionally, practices such as wearing UV-protective sunglasses and taking breaks from screens can help protect the eyes.Regular eye exams are essential for assessing the operation of the eye and detecting any potential issues early on.
Effects of Aging on Vision:
As we age, our vision naturally changes. Common age-related eye conditions include cataracts, glaucoma, and age-related macular degeneration. Regular eye exams become even more critical as we get older to monitor and manage these conditions effectively.
Signs of Eye Problems:
Symptoms such as blurry vision, eye pain, redness, and sensitivity to light may indicate underlying eye problems. It’s essential to recognize these signs and seek prompt medical attention to prevent further complications.
Preventive Measures for Eye Health:
Taking preventive measures can help maintain good eye health. This includes wearing protective eyewear during activities that pose a risk of eye injury and eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and nutrients beneficial for vision.
Importance of Nutrition for Eye Health:
Nutrition plays a vital role in supporting eye health. Foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins A, C, and E can help protect against age-related eye diseases. Supplements such as lutein and zeaxanthin may also benefit vision.
Technological Advancements in Eye Care:
Advances in technology have revolutionized eye care, with treatments such as laser eye surgery offering precise vision correction. Additionally, innovations in lens design and treatments for conditions like dry eye have improved outcomes for patients.
Caring for Your Eyes in the Digital Age:
In today’s digital world, prolonged screen time can strain the eyes and contribute to symptoms like dryness and eyestrain. Practicing good habits such as taking regular breaks, adjusting screen brightness, and maintaining proper posture can help alleviate these symptoms.
Eye Safety at Work and Home:
Both at work and home, it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Wearing protective eyewear when engaging in activities such as woodworking, sports, or using power tools can prevent eye trauma and preserve vision.
Support for Individuals with Visual Impairments:
For individuals with visual impairments, various assistive technologies and resources are available to enhance accessibility and independence. These include screen readers, magnifiers, and braille materials, highlighting the importance of inclusivity in society.
Conclusion:
Understanding the essential for maintaining good vision and eye health throughout life. By taking preventive measures, seeking regular eye care, and staying informed about advances in eye care, individuals can protect their vision and enjoy optimal visual function.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions):
1.How often should I have an eye exam?
It’s recommended to have a comprehensive eye exam at least once every two years for adults with no known eye problems. However, individuals with existing eye conditions or risk factors may need more frequent exams.
2.Can eye exercises improve vision?
While eye exercises may help alleviate symptoms of eye strain, they typically do not improve vision or correct refractive errors. It’s essential to consult an eye care professional for personalized recommendations.
3.Are there natural remedies for dry eyes?
Yes, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage dry eye symptoms.