Introduction:
The eyes are misaligned in squint eye, also known as strabismus, due to an imbalance in the muscles responsible for eye movement. It can affect people of all ages, and if left untreated, it may lead to vision problems and even affect self-esteem. While surgery is a common treatment option for squint eye, there are also non-surgical alternatives available that can effectively address the condition. In this article, we will explore some of these non-surgical treatments and their effectiveness in managing squint eye.
Understanding Squint Eye:
Moreover, squint eye occurs when the muscles responsible for eye movement are imbalanced, resulting in the eyes pointing in different directions. Furthermore, it can cause the affected eye to turn inward, outward, upward, or downward. Consequently, this misalignment can lead to various complications such as double vision, reduced depth perception, and eye strain.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Squint Eye:
1. Vision Therapy:
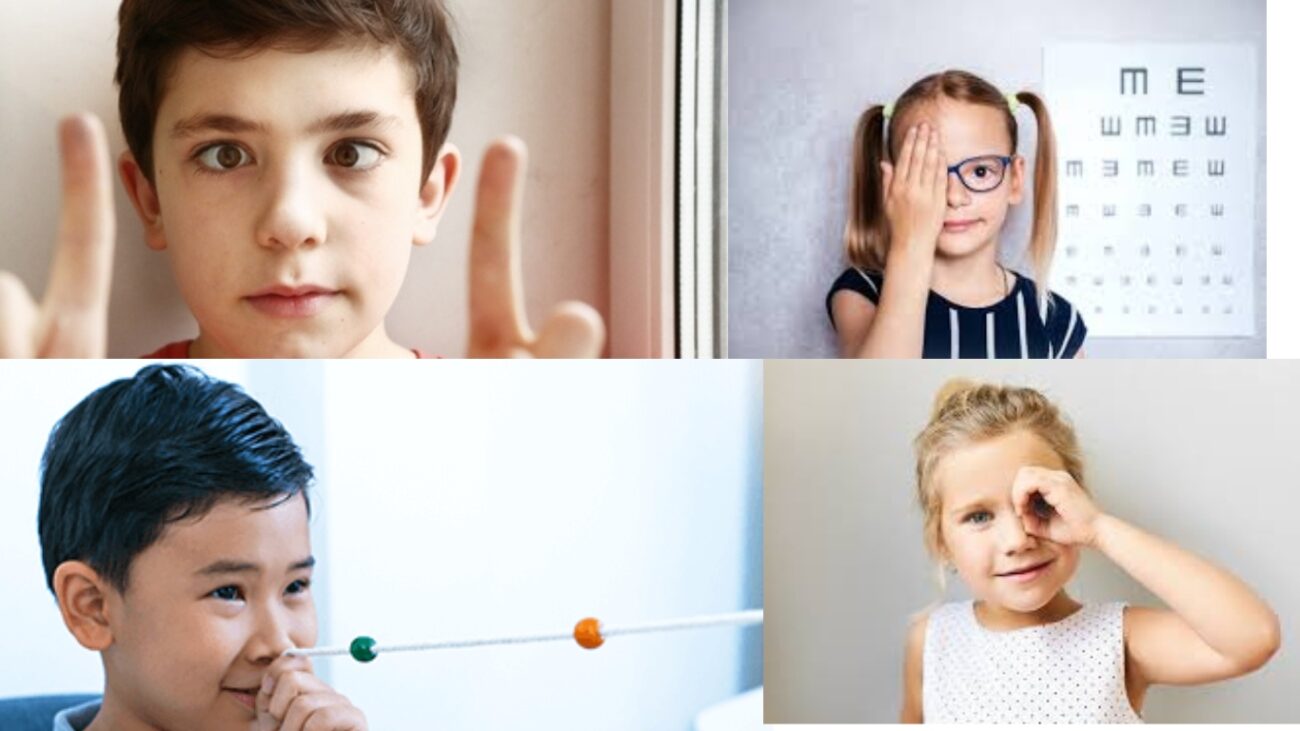

Vision therapy is a non-surgical treatment option that aims to improve eye coordination and strengthen the eye muscles. It involves a series of exercises and activities tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Through regular sessions with a trained optometrist or ophthalmologist, patients can enhance their eye alignment and improve binocular vision.
2. Eye Patching:
Moreover, ophthalmologists commonly use eye patching as a non-surgical treatment for squint eye, particularly in children. It involves covering the stronger eye with a patch, forcing the weaker eye to work harder and strengthen its muscles. Patching helps in training the eyes to work together and can be an effective way to correct mild to moderate squint eye.
3. Prism Glasses:
Prism glasses are another non-surgical alternative for managing squint eye. These specialized glasses contain prisms that alter the direction of light entering the eyes, redirecting it to the appropriate areas of the retina. By doing so, prism glasses can help align the eyes and improve binocular vision. Ophthalmologists often prescribe eye patches for individuals with specific types of squint eye or for those who are not suitable candidates for surgery.
4. Botox Injections:
In certain cases of squint eye, Botox injections can be used as a non-surgical treatment option. Botox works by temporarily weakening the overactive eye muscles, allowing the weaker muscles to regain strength and alignment. The effects of Botox injections are temporary and may require repeat treatments over time.
5. Medications:
Additionally, in certain cases, ophthalmologists may prescribe medications such as eye drops or oral medications as part of the treatment plan for squint eye. These medications, in turn, are typically used to manage underlying conditions that contribute to the misalignment, such as refractive errors or muscle spasms.
6. Orthoptic Exercises:
Orthoptic exercises involve a series of eye movements and visual activities designed to improve eye coordination and strengthen eye muscles. These exercises are usually performed under the guidance of a trained professional and can be beneficial in managing squint eye, particularly in children.
Choosing the Right Treatment:
The choice of non-surgical treatment for squint eye depends on several factors, including the severity of the condition, age of the patient, and the underlying cause. It is essential to consult with an eye care specialist who can evaluate the individual case and recommend the most suitable treatment option.
Benefits of Non-Surgical Treatments:
Squint eye treatment without surgery offer several advantages over surgical interventions. Some of the benefits include:
- Non-invasive: Non-surgical treatments do not involve incisions or surgical procedures, minimizing the associated risks and complications.
- Furthermore, non-surgical options are often more cost-effective than surgery, thereby making them accessible to a wider range of individuals.
- Conservative approach: Non-surgical treatments allow for a conservative approach, reserving surgery as a last resort or for cases that cannot be effectively managed by non-invasive methods.
- Minimal downtime: Unlike surgery, non-surgical treatments typically require little to no downtime, allowing individuals to resume their daily activities shortly after the procedure.
Conclusion:
Nonetheless, non-surgical treatments offer effective alternatives to surgery for managing squint eye. Various options, such as vision therapy, eye patching, prism glasses, Botox injections, medications, and orthoptic exercises, are available as non-invasive approaches. The choice of treatment, however, depends on the individual’s specific condition and should be made in consultation with an eye care professional. Furthermore, these non-surgical approaches not only improve eye alignment but also contribute significantly to better vision and overall quality of life for individuals with squint eye.
FAQs:
1. Are non-surgical treatments as effective as surgery for squint eye?
Moreover, non-surgical treatments can be highly effective, particularly for mild to moderate squint eye. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness may vary depending on the individual case. Therefore, it is essential to consult with an eye care specialist for an accurate assessment and appropriate recommendation.
2. How long does vision therapy typically take to show results?
The duration of vision therapy varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment. It can range from several weeks to several months. Consistency and adherence to the prescribed therapy plan are crucial for achieving optimal results.
3. Can adults benefit from non-surgical treatments for squint eye?
Yes, non-surgical treatments can benefit adults with squint eye. The suitability of specific treatments may vary based on the individual case, and it is advisable to consult with an eye care professional for personalized recommendations.
4. Are there any side effects associated with Botox injections for squint eye?
Temporary side effects such as redness, bruising, or drooping of the eyelid may occur after Botox injections. These effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days or weeks.
5. Can non-surgical treatments completely cure squint eye?
While non-surgical treatments can significantly improve eye alignment and manage squint eye, it is important to note that complete cure may not be achievable in all cases. Nonetheless, the primary goal of treatment is to optimize visual function and enhance the overall quality of life.