KERATOCONUS VISION:
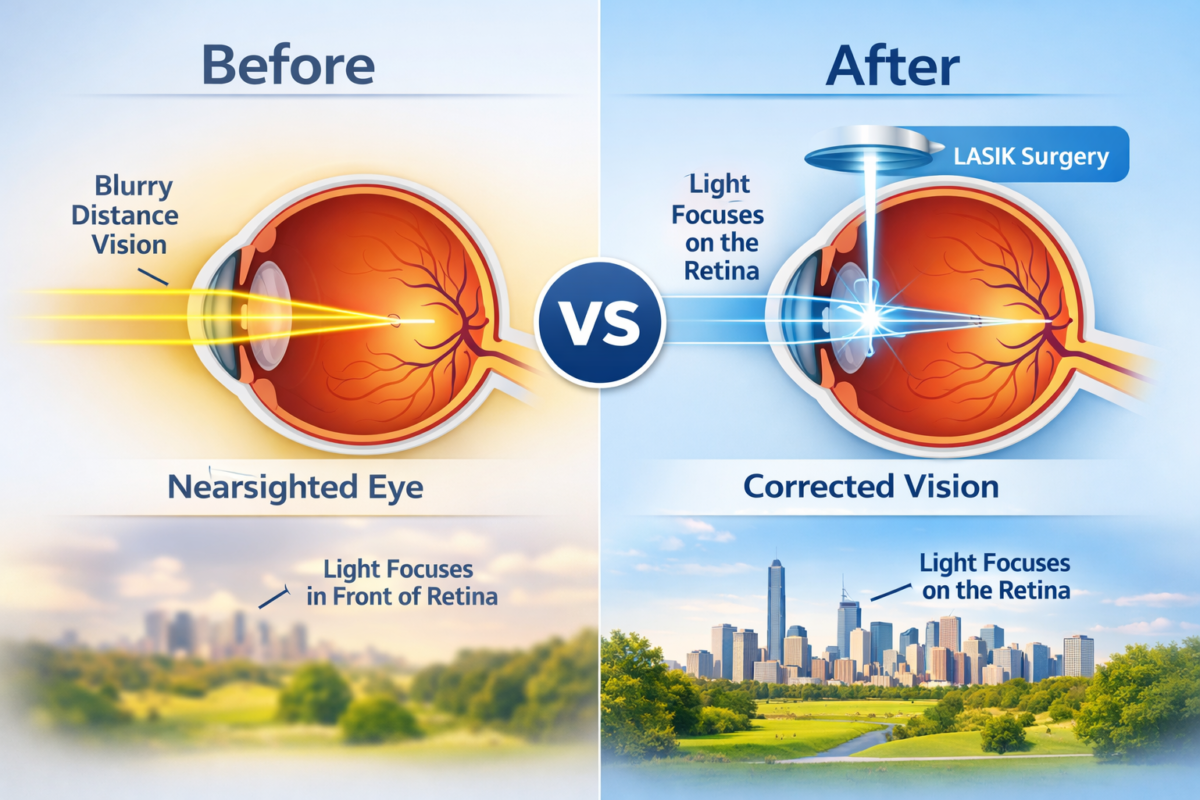
Keratoconus vision is a progressive eye disease that affects the cornea, causing it to thin and bulge into a cone-like shape. This distortion can lead to significant vision problems and, if left untreated, can severely impact a person’s quality of life.
Keratoconus :
Keratoconus is a degenerative disorder of the eye where the normally round, dome-shaped cornea becomes thin and irregularly shaped. This abnormal curvature deflects light as it enters the eye, causing distorted vision.

Causes of Keratoconus:
- Genetics: A family history of keratoconus increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Eye Rubbing: Frequent and vigorous rubbing of the eyes can weaken the corneal structure.
- Inflammatory Conditions:Eye Rubbing: Frequent and vigorous rubbing of the eyes can weaken the corneal structure. Consequently, this can lead to a variety of vision problems and increase the risk of developing conditions such as keratoconus.
- ions: Conditions such as allergies and asthma may contribute to the weakening of the corneal tissue.
- Oxidative Stress: Imbalances Oxidative Stress: Consequently, imbalances in the corneal tissue can lead to degradation and thinning of the cornea.in the corneal tissue can lead to degradation and thinning of the cornea.
Symptoms of Keratoconus:
- Blurred Vision: Vision becomes increasingly blurry; consequently, making it difficult to see clearly at any distance.
- Distorted Vision: Objects may appear stretched or wavy due to the irregular shape of the cornea.
- Increased sensitivity to light can be problematic; consequently, bright lights can cause discomfort and glare.
- Frequent Prescription Changes: Moreover, rapid changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescriptions are common as the condition progresses
- Double Vision: In some cases, double vision (monocular diplopia) may occur in one eye.
Diagnosis of Keratoconus vision:
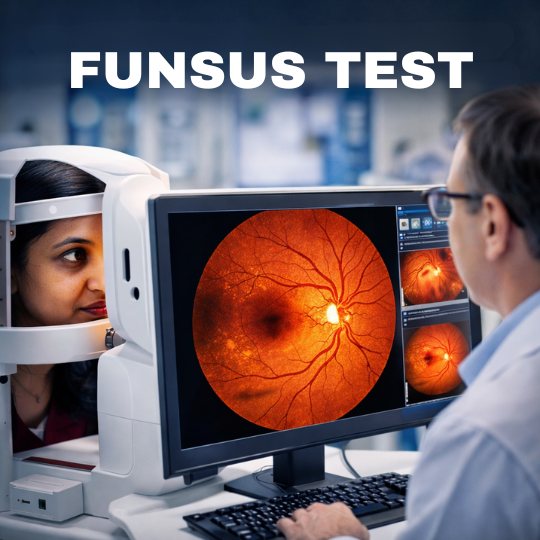
- Corneal Topography: This imaging technique maps the surface curvature of the cornea to detect any abnormalities.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: A detailed examination of the cornea using a slit lamp can reveal thinning and other characteristic changes.
- Pachymetry: This test measures the thickness of the cornea, helping to identify thinning areas.
- Keratometry: Measures the curvature of the cornea Keratoconus Vision to assess the degree of irregularity.
Treatment for keratoconus vision:
- Eyeglasses or Soft Contact Lenses: In the early stages, vision correction with eyeglasses or soft contact lenses can be effective.
- Custom Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lenses: These lenses provide a more stable and smooth surface for better vision correction.
- Scleral Lenses: Larger lenses that vault over the cornea, providing comfort and improved vision for more advanced cases.
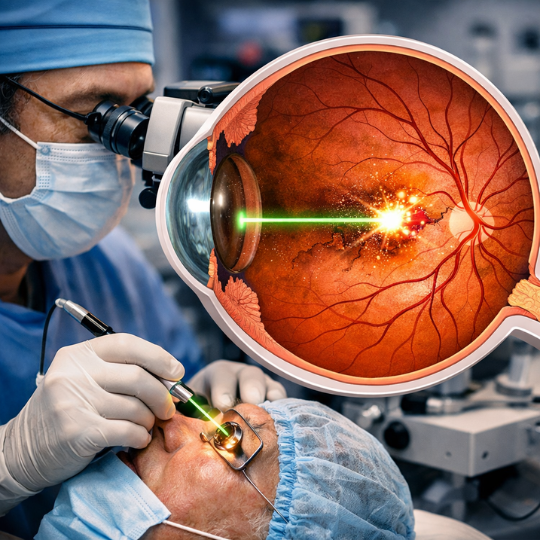
- Corneal Cross-Linking (CXL): A minimally invasive Keratoconus Vision:procedure that strengthens the corneal tissue to halt progression.
- Intacs: Small, crescent-shaped inserts placed within the cornea to help reshape it and improve vision.
- Corneal Transplant: In severe cases,Keratoconus Vision: a corneal transplant may be necessary to replace the damaged cornea with healthy donor tissue.
Author Details:
Dr. Sushruth Appajigowda holds a prominent position as a Cornea, Cataract, Glaucoma, and LASIK Surgeon in Bangalore. He serves as the chief Cataract and Refractive surgeon at Vijaya Nethralaya Eye Hospital, Nagarbhavi Bangalore. Renowned as one of the finest LASIK surgeons nationwide, he brings with him over 12+ years of experience across multiple LASIK platforms, including ZEISS, ALCON, SCHWIND, AMO, and Bausch and Lomb. Having successfully conducted over 5000 LASIK procedures, Dr. Sushruth holds the title of a Certified Refractive Surgeon and a Fellow of the All India Collegium Of Ophthalmology. Furthermore, he stands as a distinguished speaker at various National and International Forums, using his expertise to guide you in selecting the most suitable procedure based on your health requirements.

http://vijayanethralaya.com/link-in-bio/
Conclusion:
Keratoconus is a challenging eye condition, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, its impact on vision can be managed effectively. Keratoconus VisionUnderstanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring the available treatment options are crucial steps in maintaining eye health and preserving vision. Furthermore, early intervention and regular eye check-ups play a significant role in preventing potential eye diseases.