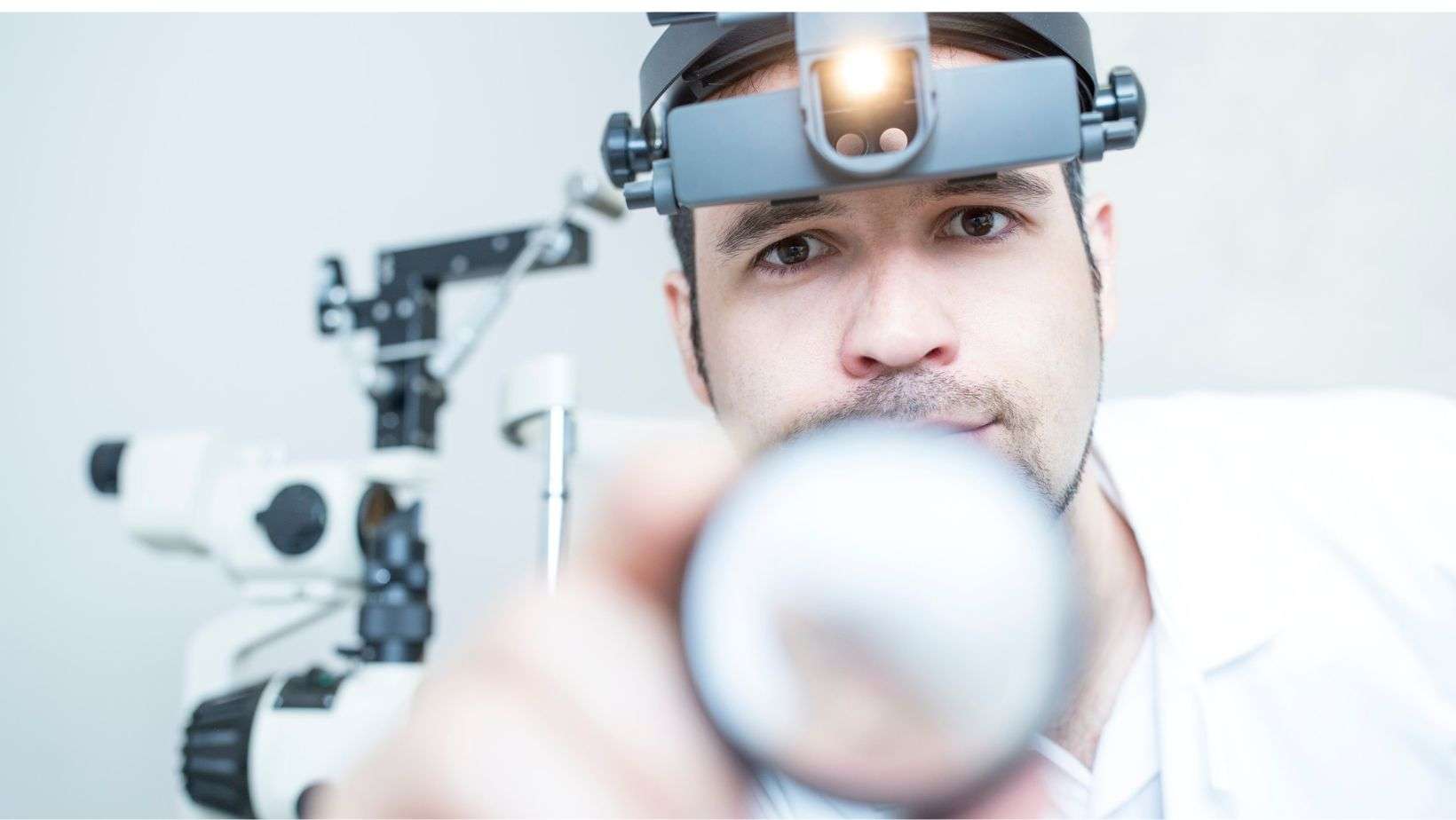
In the fast-evolving landscape of medical technology and diagnostics, ophthalmology stands as a beacon of innovation. Within this field, one remarkable tool has emerged to revolutionize the way we examine and understand the human eye – Indirect Ophthalmoscopy. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of this technique, its applications, and how it can empower healthcare professionals to make informed decisions.
Unveiling the Basics of Indirect Ophthalmoscopy:
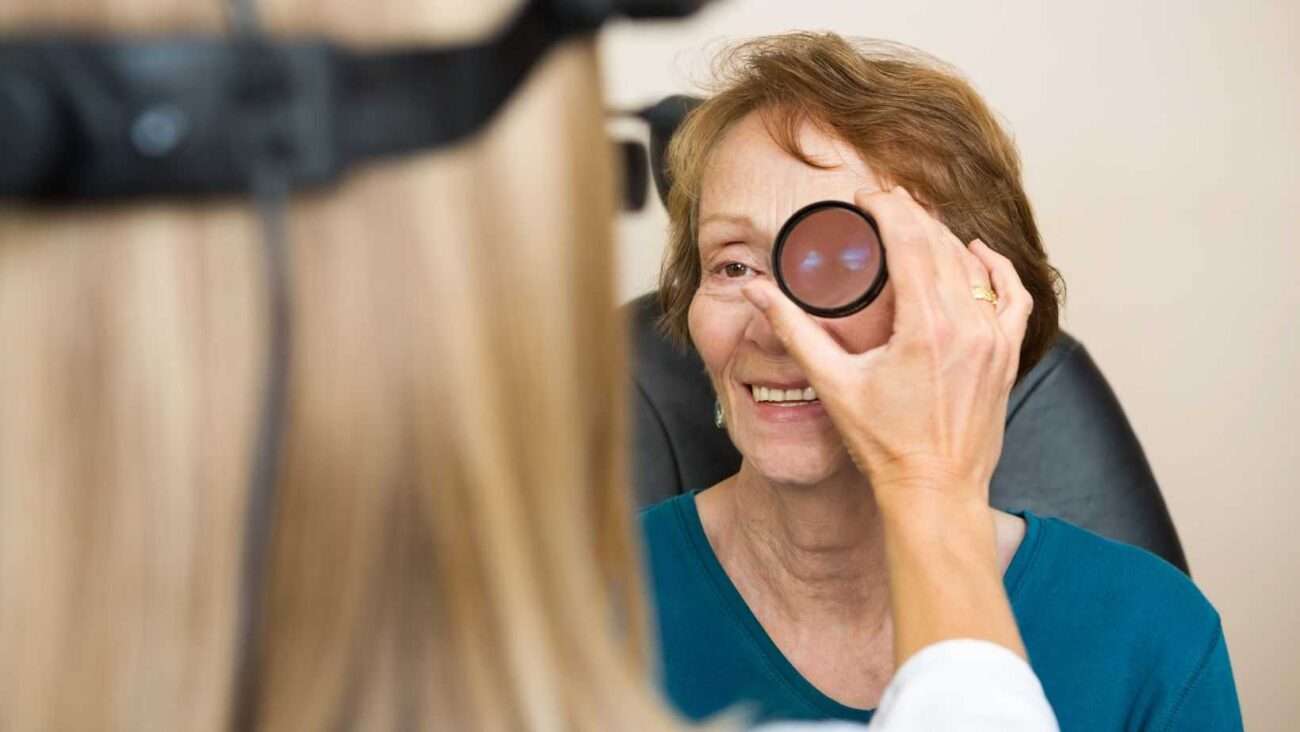
What is Indirect Ophthalmoscopy?
Indirect Ophthalmoscopy, often referred to as the “gold standard” of eye examination, is a non-invasive diagnostic method used by ophthalmologists to visualize the retina, optic nerve, and vitreous humor. Unlike its direct counterpart, which requires the patient’s eye to be in close proximity to the instrument, indirect ophthalmoscopy employs a condensing lens and a light source to view the eye’s interior through a dilated pupil.
The Magic of the Condensing Lens:
The key to the effectiveness of indirect ophthalmoscopy lies in the condensing lens. This lens not only magnifies the view but also provides a wider field of vision, allowing clinicians to spot abnormalities or anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed. Its versatility makes it an indispensable tool in various ophthalmic procedures.
Applications of Indirect Ophthalmoscopy:
Diagnosis of Retinal Disorders:
This is an invaluable tool for diagnosing a wide range of retinal disorders. Conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, and retinal detachment can be identified in their early stages, leading to prompt treatment and better patient outcomes.
Monitoring Progression:
For patients with chronic eye conditions, regular indirect ophthalmoscopy examinations are crucial for monitoring disease progression. Furthermore, by visualizing subtle changes in the retina over time, clinicians can adjust treatment plans and ensure the best possible care.
Advantages:
Non-Invasiveness:
One of the most significant advantages of indirect ophthalmoscopy is its non-invasive nature. Patients experience minimal discomfort during the procedure, making it suitable for individuals of all ages.
Comprehensive Examination:
The wide field of view provided by the condensing lens allows for a comprehensive examination of the retina, optic nerve, and vitreous humor. This comprehensive approach enables the early detection of potentially sight-threatening conditions.
Tips for an Effective Indirect Ophthalmoscopy Examination:
Proper Patient Preparation:
To ensure a successful examination, proper patient preparation is essential. This includes pupil dilation using appropriate eye drops and ensuring a darkened room for optimal visualization.
Skill and Expertise:
Mastering the art of indirect ophthalmoscopy requires skill and expertise. Additionally, healthcare professionals must undergo specialized training to perform this procedure accurately.
The Future of Ophthalmic Diagnosis:
As technology continues to advance, we can expect further enhancements in indirect ophthalmoscopy. Innovations such as digital imaging and artificial intelligence integration are already shaping the future of ophthalmic diagnosis, promising even more precise and efficient examinations.
Conclusion:
This has emerged as an indispensable tool in the field of ophthalmology. Furthermore, its non-invasive nature, comprehensive examination capabilities, and the ability to diagnose and monitor various eye conditions make it a cornerstone of modern eye care. As we look ahead, the synergy between technology and medicine promises to elevate the standards of ophthalmic diagnosis. Consequently, this will ensure brighter and clearer visions for all.

