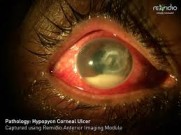
Hypopyon is a condition where pus accumulates in the anterior chamber of the eye, which is the space between the cornea and the iris. This accumulation of pus gives the anterior chamber a cloudy appearance, which can be observed during a clinical eye examination.
Symptoms of Hypopyon:
- Blurred vision
- Eye pain or discomfort
- Redness in the affected eye
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Decreased vision clarity
- Excessive tearing
- Floating spots or specks in vision (floaters)
Causes of Hypopyon:
- Bacterial infections, such as bacterial keratitis or endophthalmitis, require prompt medical attention to prevent potential complications and preserve vision.
- Fungal infections can vary widely in severity, ranging from superficial skin conditions to systemic diseases affecting multiple organs.
- Viral infections like herpes simplex virus (HSV) or varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
- Trauma to the eye
- Inflammatory conditions such as uveitis or Behçet’s disease
- Complications from eye surgeries can range from minor issues such as temporary discomfort and dry eyes to more serious complications like infection, inflammation, or even vision loss.
- Systemic diseases like tuberculosis or autoimmune disorders
Diagnosis of Hypopyon:
- Visual acuity test
- Slit-lamp examination to assess the anterior chamber and other structures of the eye
- Intraocular pressure measurement
- Corneal scraping or culture to identify the causative organism in cases of infection
- Blood tests or imaging studies to evaluate systemic conditions associated with hypopyon
Treatment:
- Antibiotic or antifungal eye drops or ointments to treat infections
- Systemic antibiotics or antiviral medications for severe infections
- Corticosteroid eye drops to reduce inflammation
- Anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressive agents for autoimmune-related hypopyon
- Surgical intervention, such as drainage of the pus or vitrectomy in cases of severe infection or inflammation
- Management of underlying systemic conditions contributing to hypopyon.
Prevention:
- Practicing good eye hygiene and avoiding eye trauma.
- Using protective eyewear during activities that pose a risk of eye injury.
- Seeking prompt treatment for eye infections or injuries.
- Managing systemic conditions effectively through regular medical care and medication adherence.
Author Details:
Dr. Sushruth Appajigowda holds a prominent position as a cornea, cataract, glaucoma, and LASIK surgeon in Bangalore. He serves as the chief cataract and refractive surgeon at Vijaya Nethralaya Eye Hospital, Nagarbhavi, Bangalore. Renowned as one of the finest LASIK surgeons nationwide, he brings with him over 12 years of experience across multiple LASIK platforms, including ZEISS, ALCON, SCHWIND, AMO, and Bausch and Lomb. Having successfully conducted over 5000 LASIK procedures, Dr. Sushruth holds the title of a Certified Refractive Surgeon and a Fellow of the All India Collegium of Ophthalmology. Furthermore, he stands as a distinguished speaker at various national and international forums, using his expertise to guide you in selecting the most suitable procedure based on your health requirements.

https://vijayanethralaya.com/link-in-bio/
Conclusion:
Hypopyon is a serious eye condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate management to prevent complications and preserve vision. By understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for hypopyon, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their ocular health and seek prompt medical attention if needed.