Central scotoma refers to a specific type of vision impairment characterized by a blind spot in the center of the visual field. Unlike peripheral vision loss, which affects the outer edges of vision, central scotoma impacts the central area, crucial for tasks such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces.

Causes of Central Scotoma:
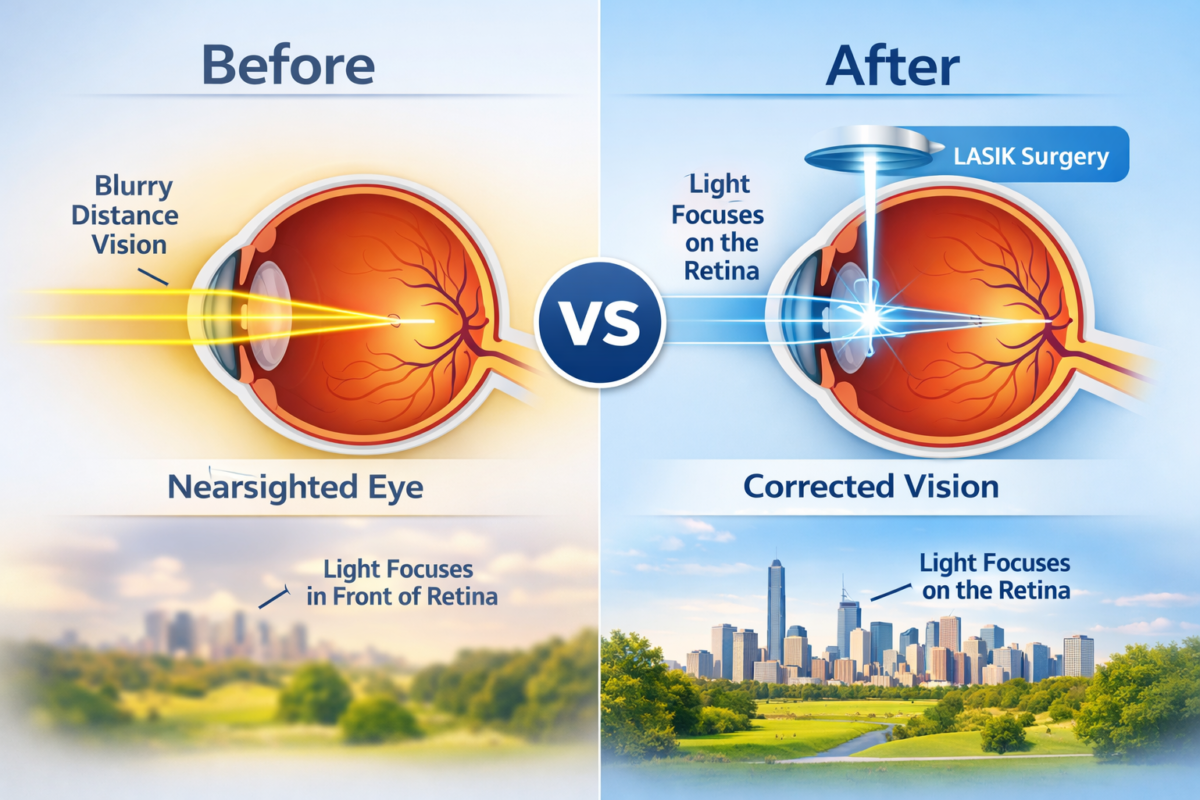
- Macular Degeneration: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of central vision loss and central scotoma among older adults. It occurs when the macula, a small but critical part of the retina responsible for central vision, deteriorates.
- Optic Nerve Damage: Damage to the optic nerve, often due to conditions like glaucoma or optic neuritis, can result in central scotoma. The optic nerve carries visual information from the retina to the brain, and any impairment can lead to visual disturbances.
- Retinal Disorders: Various retinal disorders, such as diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, and retinitis pigmentosa, can cause central scotoma by affecting the macula or surrounding retinal tissues.
- Head injuries or trauma to the eye can result in central scotoma if the impact damages the optic nerve, retina, or other crucial structures involved in vision. Moreover, such injuries may lead to significant visual impairment, including central scotoma, due to the disruption of vital components of the visual system.
Symptoms of Central Scotoma:
- Blurred or distorted central vision
- Difficulty reading or recognizing faces
- A dark or blank spot in the center of vision
- Objects appearing smaller or larger than they are
- Difficulty with tasks requiring detailed vision, such as sewing or drawing
Diagnosis and Treatment:
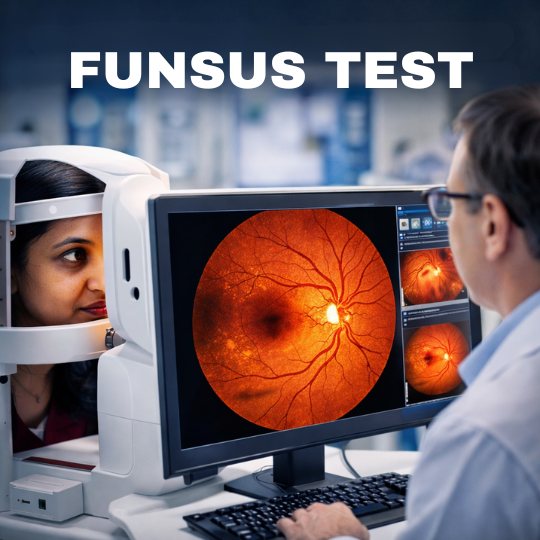
Diagnosing central scotoma typically involves a comprehensive eye examination. This examination includes visual acuity tests, dilated eye exams, and imaging tests like optical coherence tomography (OCT) or fundus photography to assess the retina and optic nerve. Furthermore, these diagnostic procedures help clinicians to accurately identify the presence and extent of central scotoma resulting from head injuries or trauma to the eye.
Treatment options for central scotoma vary depending on the underlying cause:
- AMD Management: For AMD-related , treatments may include anti-VEGF injections, photodynamic therapy, or implantable devices to improve vision and slow disease progression.
- Glaucoma Control: Managing intraocular pressure through medication, laser therapy, or surgery can help prevent further optic nerve damage and preserve remaining vision.
- Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment: Controlling blood sugar levels and receiving timely interventions such as laser therapy or intravitreal injections can prevent progression in diabetic patients.
- Vision Rehabilitation: Visual aids such as magnifiers, telescopic lenses, or electronic devices can assist individuals with in performing daily tasks more effectively.
Author Details:
Dr. Sushruth Appajigowda holds a prominent position as a Cornea, Cataract, Glaucoma, and LASIK Surgeon in Bangalore. He serves as the chief Cataract and Refractive surgeon at Vijaya Nethralaya Eye Hospital, Nagarbhavi Bangalore. Renowned as one of the finest LASIK surgeons nationwide, he brings with him over 12+ years of experience across multiple LASIK platforms, including ZEISS, ALCON, SCHWIND, AMO, and Bausch and Lomb. Having successfully conducted over 5000 LASIK procedures, Dr. Sushruth holds the title of a Certified Refractive Surgeon and a Fellow of the All India Collegium Of Ophthalmology.

http://vijayanethralaya.com/link-in-bio/
Conclusion:
It presents significant challenges to individuals affected by this condition, impacting their quality of life and independence. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for early detection and intervention.