What is Avastin Injection used for?
Doctors initially developed Avastin (Bevacizumab) to treat cancer, but it has recently become widely used in ophthalmology. They use it to treat several eye conditions, particularly those related to the retina.
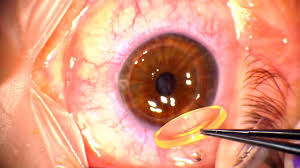
The retina is the thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye that is responsible for transmitting visual signals to the brain. Diseases that affect the retina can lead to vision loss or blindness. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one such condition, and it is the leading cause of blindness in people over 50 years old in developed countries. Other conditions include diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion, and choroidal neovascularization.
Doctors use Avastin to treat these conditions by inhibiting the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. These abnormal blood vessels are a hallmark of many retinal diseases, and they can cause damage to the surrounding tissue by leaking fluid or bleeding. Avastin injection works by blocking a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) that is responsible for the growth of these abnormal blood vessels.
Avastin injection:
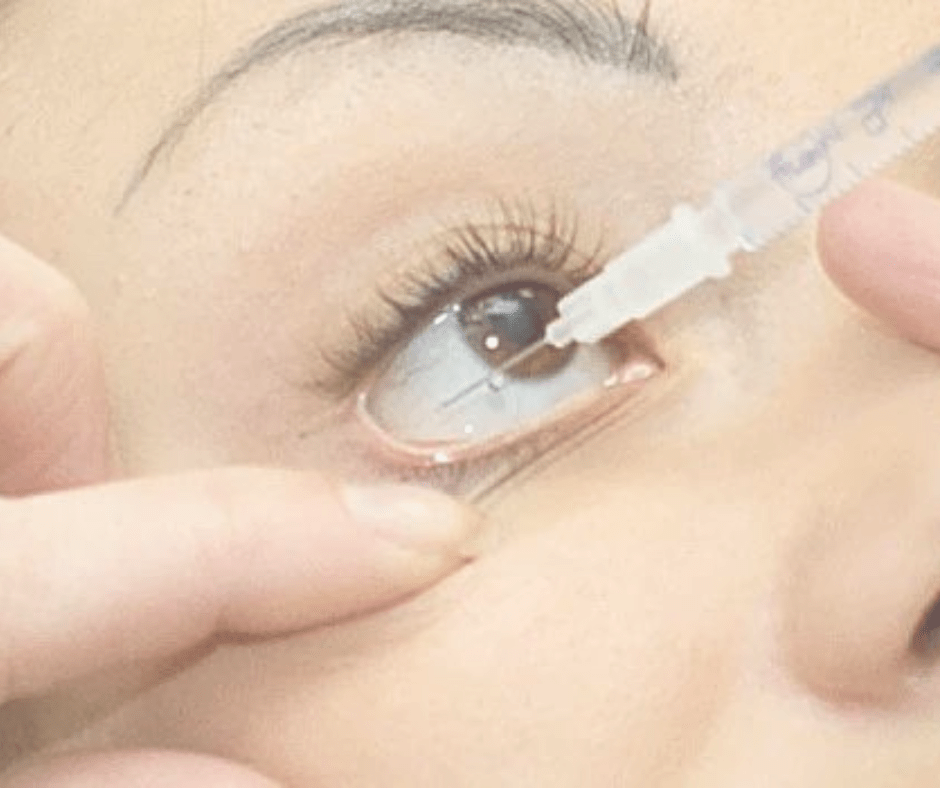
Doctors administer the Avastin injection directly into the eye. Though the procedure may sound uncomfortable, they perform it under local anesthesia, and patients typically feel minimal discomfort. They complete the injection in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to return home the same day.
Ophthalmologists commonly use Avastin injections off-label, even though the FDA has not officially approved them for ophthalmology. Numerous clinical trials and real-world experience have established the safety and efficacy of Avastin in treating retinal diseases.
One of the advantages of using Avastin injection over other medications is its cost. Avastin costs significantly less than other FDA-approved drugs, such as Lucentis and Eylea, used to treat retinal diseases.This has made it a popular choice for patients who may not have insurance coverage for these more expensive drugs.
Avastin is a powerful medication that has revolutionised the treatment of retinal diseases. Although doctors initially developed it for cancer treatment, they have found Avastin to be valuable in ophthalmology. Patients suffering from retinal diseases should discuss with their ophthalmologist whether Avastin is a good option.
Diabetic retinopathy:
It is a serious complication of diabetes that affects the eyes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, which is the part of the eye that detects light and sends signals to the brain. If left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can cause vision loss and even blindness. Doctors have shown that Avastin (Bevacizumab) is effective in treating diabetic retinopathy.
Avastin works by inhibiting the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. These abnormal blood vessels are a hallmark of diabetic retinopathy and can cause damage to the retina by leaking fluid or bleeding. Avastin blocks a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is responsible for the growth of these abnormal blood vessels. By blocking VEGF, Avastin can prevent the progression of diabetic retinopathy and even improve vision.
Clinical studies have shown that Avastin is effective in treating diabetic retinopathy. In one study, doctors treated patients with diabetic macular edema (a type of diabetic retinopathy) using Avastin, and those patients showed significant improvement in visual acuity compared to those who received a placebo injection. Another study found that Avastin was effective in reducing the number of abnormal blood vessels in the retina in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Doctors typically administer Avastin via injection directly into the eye. While it may sound uncomfortable, they perform the procedure under local anesthesia, and patients often report minimal discomfort. They carry out the injection in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to return home the same day.
Advantage of avastin:
One of the advantages of using Avastin over other medications is its cost. Avastin costs significantly less than other FDA-approved drugs for treating diabetic retinopathy, such as Lucentis and Eylea. This has made it a popular choice for patients who may not have insurance coverage for these more expensive drugs.
Avastin is a valuable tool in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. It is effective in preventing the progression of the disease and improving vision. Patients who are suffering from diabetic retinopathy should discuss with their ophthalmologist whether Avastin is a good option for them. As with any medical treatment, it is important to weigh the benefits and risks of the medication with your doctor.
Branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO):
It is a common eye condition that occurs when a vein in the retina becomes blocked, leading to vision loss. The blockage causes blood to build up in the retina, which can damage the surrounding tissue. Avastin (Bevacizumab) is a medication that has been shown to be effective in treating BRVO.
Avastin works by inhibiting the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. These abnormal blood vessels are a hallmark of BRVO and can cause damage to the retina by leaking fluid or bleeding. Avastin blocks a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is responsible for the growth of these abnormal blood vessels. By blocking VEGF, Avastin can prevent the progression of BRVO and even improve vision.
Clinical studies have shown that Avastin is effective in treating BRVO. In one study, doctors treated patients with macular edema due to BRVO using Avastin, and these patients showed significant improvement in visual acuity compared to those who received a placebo injection. Another study found that Avastin was effective in reducing the thickness of the retina in patients with BRVO.
Doctors typically administer Avastin via injection directly into the eye. While it may sound uncomfortable, they perform the procedure under local anesthesia, and patients often report minimal discomfort. They usually perform the injection in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to return home the same day.
One of the advantages of using Avastin over other medications is its cost. Avastin is significantly less expensive than other drugs that are FDA-approved for the treatment of BRVO, such as Lucentis and Eylea. This has made it a popular choice for patients who may not have insurance coverage for these more expensive drugs.
conclusion:
Avastin is a valuable tool in the treatment of BRVO. It has been shown to be effective in preventing the progression of the disease and improving vision. Patients who are suffering from BRVO should discuss with their ophthalmologist whether Avastin is a good option for them. As with any medical treatment, it is important to weigh the benefits and risks of the medication with your doctor.
Neovascular glaucoma (NVG):
is a serious eye condition that occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow on the iris and block the flow of fluid out of the eye, leading to increased eye pressure and damage to the optic nerve. Avastin (Bevacizumab) is a medication that has been shown to be effective in treating NVG.
Avastin works by inhibiting the growth of abnormal blood vessels. In the case of NVG, the abnormal blood vessels on the iris are a result of ischemia, or lack of blood flow, to the area. This ischemia causes the release of growth factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which stimulates the growth of new blood vessels. Avastin blocks VEGF, preventing the growth of these abnormal blood vessels and reducing eye pressure.
Clinical studies have shown that Avastin is effective in treating NVG. In one study, doctors treated patients with NVG using Avastin, and these patients showed a significant reduction in eye pressure compared to those who received a placebo injection. Another study found that Avastin was effective in reducing the number of abnormal blood vessels on the iris in patients with NVG.
Doctors typically administer Avastin via injection directly into the eye. Although the procedure may sound uncomfortable, they perform it under local anesthesia, and patients often report minimal discomfort. They usually carry out the injection in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to return home the same day.
Avastin injection cost
One of the advantages of using Avastin over other medications is its cost. Avastin costs significantly less than other FDA-approved drugs for treating NVG, such as Lucentis and Eylea. This has made it a popular choice for patients who may not have insurance coverage for these more expensive drugs.
In conclusion, Avastin is a valuable tool in the treatment of neovascular glaucoma. It is effective in reducing eye pressure and preventing the progression of the disease. Patients who are suffering from NVG should discuss with their ophthalmologist whether Avastin is a good option for them. As with any medical treatment, it is important to weigh the benefits and risks of the medication with your doctor.
Diabetic macular edema (DME):
It is a common eye condition that occurs in people with diabetes. Fluid accumulation in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for clear, detailed vision, causes DME. Doctors use Avastin (Bevacizumab), a medication proven effective in treating DME.
Avastin works by inhibiting the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. In the case of DME, the abnormal blood vessels leak fluid into the macula, causing swelling and vision loss. Avastin blocks a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is responsible for the growth of these abnormal blood vessels. By blocking VEGF, Avastin can reduce the leakage of fluid into the macula, improving vision.
Clinical studies have shown that Avastin is effective in treating DME. In one study, doctors treated patients with DME using Avastin, and these patients showed significant improvement in visual acuity compared to those who received a placebo injection. Another study found that Avastin was effective in reducing the thickness of the retina in patients with DME.
Doctors typically administer Avastin via injection directly into the eye. Although it may sound uncomfortable, they perform the procedure under local anesthesia, and patients often report minimal discomfort. They usually perform the injection in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to return home the same day.
One of the advantages of using Avastin over other medications is its cost. Avastin costs significantly less than other FDA-approved drugs for treating DME, such as Lucentis and Eylea. This has made it a popular choice for patients who may not have insurance coverage for these more expensive drugs.
conclusion:
Avastin is a valuable tool in the treatment of diabetic macular edema. It has been shown to be effective in reducing vision loss and improving visual acuity. Patients who are suffering from DME should discuss with their ophthalmologist whether Avastin is a good option for them. As with any medical treatment, it is important to weigh the benefits and risks of the medication with your doctor.
How long does it take to improve vision after Avastin injection?
The timeline for vision improvement after an Avastin injection varies depending on the individual and the specific eye condition being treated.
In some cases, patients may notice an improvement in their vision within a few days to a week after the injection. This is especially true in cases of neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD) or macular edema, where the injection reduces swelling in the macula and improves central vision.
However, in other cases, such as with diabetic retinopathy or retinal vein occlusion, it may take several weeks to a few months to see improvement in vision. These conditions often damage the retinal tissue, and the injection aims to prevent further damage and promote healing rather than directly improve vision.
It is important to note that not all patients will experience improvement in vision after an Avastin injection. While the medication has been shown to be effective in many cases, individual results may vary. Additionally, some patients may require multiple injections over time to achieve optimal results.
The timeline for vision improvement after an Avastin injection varies and depends on the specific condition being treated and the individual’s response to the medication. Patients should discuss their expectations and timeline for improvement with their ophthalmologist.
How many Avastin injections will I need?
The number of Avastin injections you need depends on several factors, including the specific eye condition being treated, the severity of the condition, and your individual response to the medication.
In many cases, doctors administer Avastin injections monthly, with a series of injections given over several months. The goal of treatment is to reduce swelling or abnormal blood vessel growth in the eye and improve vision. The number of injections needed may vary, depending on how well the medication is working and how severe the condition is.
For example, in the case of macular degeneration, patients may require an initial series of three monthly injections, followed by ongoing injections every four to six weeks as needed. For diabetic retinopathy, treatment may involve a series of injections given every four to six weeks for several months.
It is important to note that Avastin injections do not offer a permanent cure for eye conditions, but rather provide ongoing management and treatment to help prevent vision loss and other complications. Regular follow-up appointments with your ophthalmologist are important to monitor your condition and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Ultimately, the number of Avastin injections you may need is determined on an individual basis by your healthcare provider. It is important to discuss your treatment plan with your doctor and ask any questions you may have about the duration and frequency of Avastin injections.
Author Details:
Dr. Sushruth Appajigowda holds a prominent position as a Cornea, Cataract, Glaucoma, and LASIK Surgeon in Bangalore. He serves as the chief Cataract and Refractive surgeon at Vijaya Nethralaya Eye Hospital, Nagarbhavi Bangalore. Renowned as one of the finest LASIK surgeons nationwide, he brings with him over 12+ years of experience across multiple LASIK platforms, including ZEISS, ALCON, SCHWIND, AMO, and Bausch and Lomb. Having successfully conducted over 5000 LASIK procedures, Dr. Sushruth holds the title of a Certified Refractive Surgeon and a Fellow of the All India Collegium Of Ophthalmology. Furthermore, he stands as a distinguished speaker at various National and International Forums, using his expertise to guide you in selecting the most suitable procedure based on your health requirements.