Introduction:
Astigmatism is a refractive error that affects both children and adults. It is estimated that approximately 30% of the global population has some degree of astigmatism. Understanding this eye condition is crucial for individuals seeking clear vision and improved quality of life.
Astigmatism Meaning:
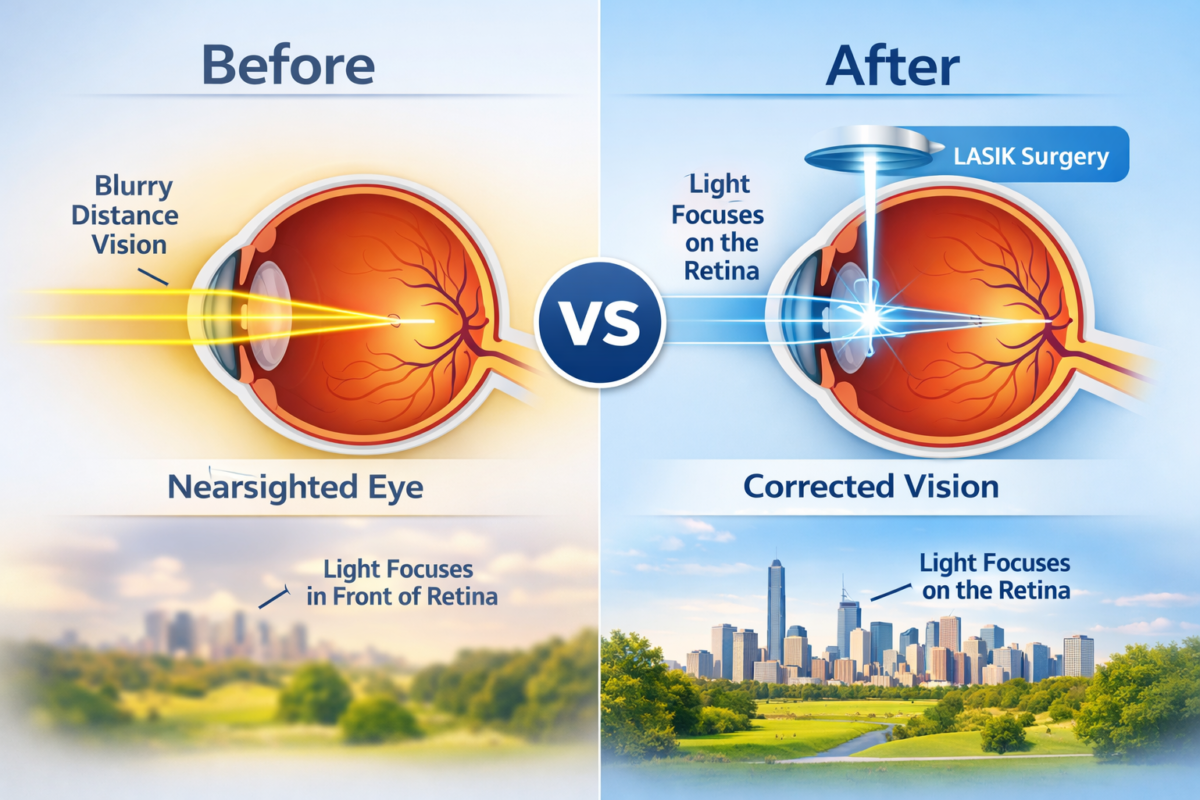
Astigmatism is a visual condition that occurs when the cornea or lens has an irregular shape. The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye, while the lens is a transparent structure located behind the iris and pupil. In a normal eye, the cornea and lens have a smooth and uniform curvature, allowing light to focus precisely on the retina.

What Causes Astigmatism?
Astigmatism can be caused by several factors. It may be present at birth (congenital) or develop later in life (acquired). The exact cause of congenital astigmatism is unknown, but it is believed to be related to genetic factors. Acquired astigmatism can be caused by eye injuries, eye surgery, or corneal diseases such as keratoconus.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of astigmatism may vary from person to person but commonly include:
- Blurred Vision: Individuals with astigmatism often experience blurred vision, which can affect their ability to see objects clearly at various distances.
- Eye Strain: Astigmatism can cause eye strain as the eyes work harder to focus on objects due to the irregular curvature of the cornea or lens.
- Headaches: Persistent headaches can be a result of astigmatism, particularly when individuals strain their eyes to compensate for blurred or distorted vision.
Diagnosis:
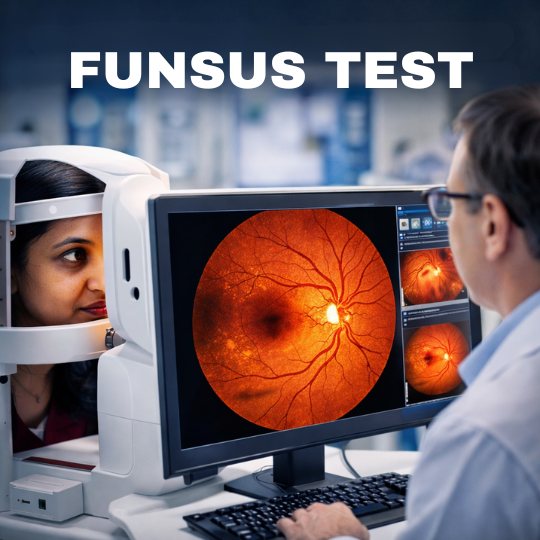
Diagnosing astigmatism requires a comprehensive eye examination performed by an eye care professional. The following tests are commonly conducted to determine the presence and severity of astigmatism:
- Comprehensive Eye Exam: A thorough examination of the eyes is conducted to assess the overall health of the eyes and identify any underlying conditions contributing to astigmatism.
- Visual Acuity Test: This test measures the sharpness and clarity of vision using an eye chart. It helps determine the degree of astigmatism and the appropriate corrective measures.
Treatment:
Astigmatism can be effectively managed through various treatment options. The most common approaches include:
- Eyeglasses and Contact Lenses: Prescription eyeglasses or contact lenses can correct astigmatism by compensating for the irregular shape of the cornea or lens.
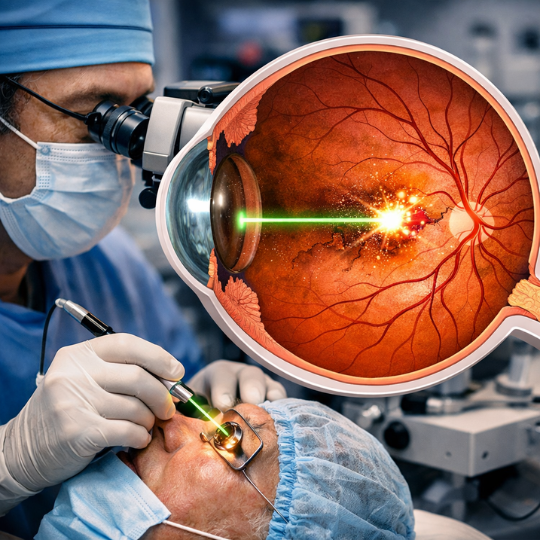
- Refractive Surgery: In some cases, refractive surgery may be recommended to permanently reshape the cornea, improving vision and reducing astigmatism.
Prevention:
While astigmatism cannot be entirely prevented, some measures can help reduce the risk or progression of the condition:
- Regular Eye Exams: Routine eye exams can detect astigmatism early on, allowing for timely intervention and appropriate management.
- Protecting Your Eyes: Taking steps to protect your eyes, such as wearing protective eyewear during sports or activities that pose a risk of eye injury, can help minimize the chances of developing astigmatism.
Conclusion:
Understanding the meaning of astigmatism is crucial for anyone seeking to gain insights into this common vision condition. By exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions about their eye health. Remember to consult with an eye care professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding astigmatism and its management.